ERP vs Cloud ERP: How to Buy the Right ERP System for Your Business in 2025
Choosing an Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) system is a big decision. The right ERP can streamline everything from inventory and finance to sales and HR in one integrated platform. But with the rise of cloud-based Software-as-a-Service (SaaS) offerings, companies must consider cloud erp systems vs cloud ERP options when planning how to buy ERP for their needs. Many businesses now explore cloud erp solutions because they offer flexibility, scalability, and reduced IT overhead compared to legacy models.
In this guide, we’ll break down what ERP is, the differences between traditional and cloud erp software, the benefits of a cloud erp system, types of solutions available, and tips on making the best purchase decision. By the end, you’ll understand the relationship between ERP and SaaS, see examples of famous ERP systems, and be ready to confidently evaluate and buy the ideal erp cloud platform for your business.
Also Read: Odoo ERP Software Development
What is ERP? Understanding Enterprise Resource Planning
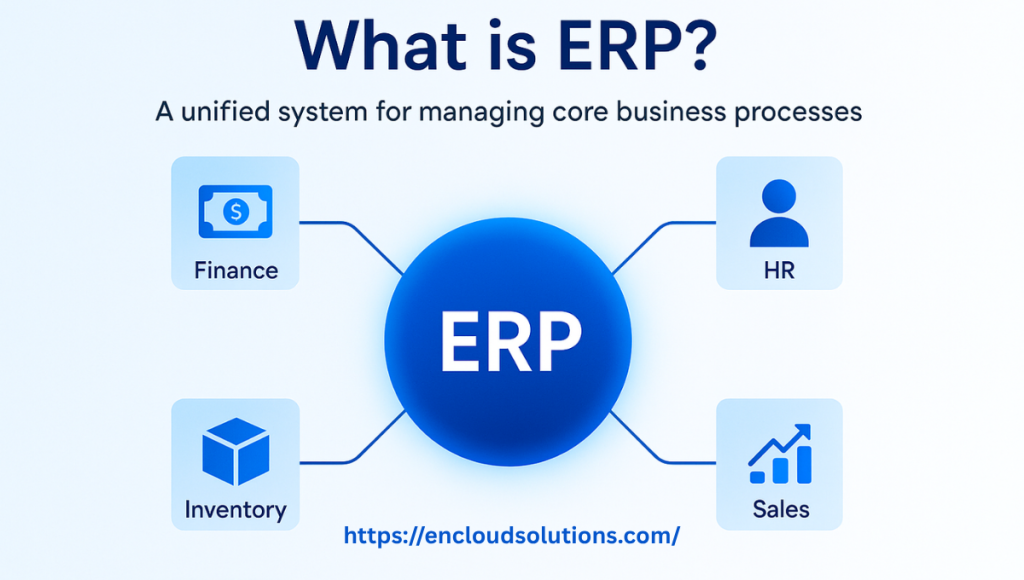
ERP stands for “enterprise resource planning,” a category of business management software that integrates all core business areas into a unified system. In practical terms, an ERP system acts as a shared database and application suite for company-wide processes, including procurement, production, inventory management, sales, marketing, finance, human resources, and more. Instead of each department using separate siloed tools, an ERP brings data and workflows together, providing a single source of truth across the organization.
In essence, ERP software is an IT system that centralizes and automates daily operations. For example, when a sale is made, the ERP can automatically update inventory levels, generate an invoice in accounting, and adjust the production schedule, all without manual data re-entry. This integrated design improves efficiency, data accuracy, and cross-department collaboration. Modern ERP solutions often include reporting and analytics features that give decision-makers real-time insights into the business. In short, what we mean by ERP is a comprehensive software platform that runs the critical processes of a company in one place, enhancing productivity and visibility.
Many ERP systems are modular, meaning you can implement the modules or applications you need (e.g., financials, supply chain, CRM) and add more over time. Whether ERP is an IT system you need depends on your business complexity. If you find your teams juggling separate spreadsheets or software for different departments, an ERP can unify these functions. Historically, ERPs were deployed on-premises (on company servers), but today ERP software is also offered in cloud-based models. This is where understanding ERP and SaaS comes in, which we’ll explore next.
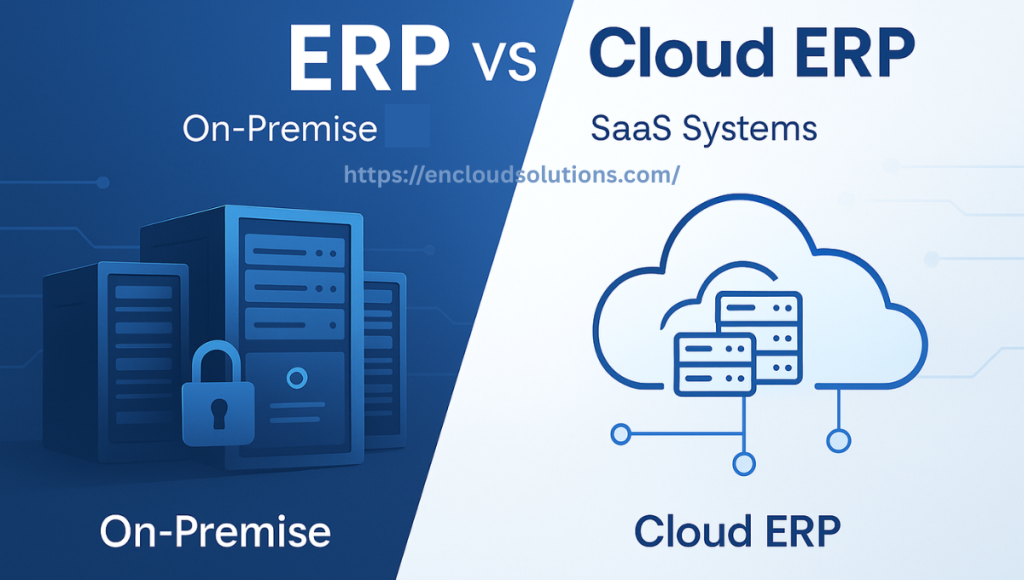
ERP vs Cloud ERP: On-Premise vs SaaS Systems
Traditional ERP systems were installed on-premise, meaning on local servers and hardware managed by the company’s IT team. Cloud erp vs on premise refers to comparing ERP software delivered as SaaS with self-hosted deployments. Both models provide the same core ERP features, but their approach differs.
1. On-Premise ERP
You purchase licenses (often at a large upfront cost) and install the software on your own servers. Your IT department is responsible for maintaining the infrastructure, handling upgrades or patches, and ensuring security. You have full control of data on-site, but also full responsibility for keeping the system running. Historically, companies would only upgrade on-prem ERP every few years due to the effort and cost involved.
2. Cloud (SaaS) ERP
You subscribe to the ERP, which is hosted on the vendor’s cloud servers and accessed via the web. The software provider manages the servers, maintenance, and updates for you. Instead of big upfront fees, you pay a monthly or annual subscription per user. The vendor rolls out improvements continuously (no waiting years for a major upgrade). This ERP and SaaS approach offloads the IT burden; you don’t need to buy hardware or dedicate staff to maintain the application. It also means your team can access the ERP anywhere with an internet connection.
To illustrate the differences, here’s a side-by-side comparison of key factors in on-premise ERP vs cloud ERP:
| Aspect | On-Premise ERP | Cloud (SaaS) ERP |
| Deployment | Installed on the company’s local servers and infrastructure. You manage it in-house. | Hosted on the vendor’s cloud servers; accessed via the internet (web browser). The provider manages the infrastructure. |
| Cost Structure | Large upfront license purchase + hardware and IT costs; recurring maintenance fees. | Subscription pricing (monthly/annual per user). Lower upfront cost; operational expense model. |
| Maintenance & Updates | Your IT team installs updates/upgrades occasionally (often every few years). You handle bug fixes and system management. | Vendor automatically updates the software regularly (often several times per year). No heavy in-house IT involvement for patches or upgrades. |
| Customization | Highly customizable (access to underlying software and databases), but extensive changes can make future upgrades harder. | Configurable settings and extensions; deep code customizations may be limited. However, frequent vendor updates add new features continuously. |
| Accessibility | Users typically access on-site or via VPN. Remote access requires a secure network setup. | Users can securely log in from anywhere, office, home, or mobile, since the system is online by design. Great for distributed teams and remote work. |
| Security | Security depends on your own IT measures (firewalls, backups, etc.). You control data locally, which can be good for strict compliance needs, but you also need to manage all risks. | Cloud providers invest heavily in security (dedicated 24/7 monitoring teams and up-to-date defenses). Data is encrypted and backed up by the vendor. Certifications (ISO, SOC, etc.) are often in place. |
As the table shows, a cloud ERP (SaaS) solution offers convenience and agility, reduced IT workload, scalable usage, and automatic innovation, while an on-premise ERP offers direct control and potentially more tailoring (at the cost of more responsibility). Importantly, both models deliver the same core ERP capabilities. Today, the trend is strongly toward cloud ERP for businesses of all sizes, unless specific regulations or offline requirements necessitate an on-premise setup. Moving to a SaaS ERP can reduce operational and capital expenses by eliminating the need to maintain your own servers and infrastructure.
If you already have an on-premise ERP, you might consider a hybrid ERP approach, keeping certain functions in-house while integrating cloud modules for new capabilities. However, many newer companies skip on-premise altogether and adopt a full cloud ERP from the start.
Benefits of Cloud ERP
Choosing cloud erp solutions has become popular because it lowers upfront costs, reduces IT workload, and gives faster access to innovation. A modern erp cloud platform ensures real-time data access, better collaboration, and stronger security compared to many in-house systems.
Companies that switch to cloud erp software often report efficiency gains, cost savings, and improved scalability. Whether you are a small business or an enterprise, adopting erp cloud systems can help your team stay competitive and agile.
1. Lower Upfront Cost & Faster ROI
With SaaS ERP, you avoid huge upfront license fees and hardware investments. You typically pay a subscription per user, which is more budget-friendly for many firms. This lowers the barrier to entry. Additionally, cloud ERP deployments tend to be faster (no physical servers to set up), meaning you start seeing value sooner. Studies even show that companies implementing ERP can reduce overall operational costs by about 23% and administrative costs by 22% on average, a testament to the efficiency gains ERP brings.
2. Reduced IT Burden & Automatic Updates
Because the vendor manages the infrastructure, your team spends far less time on maintenance. There’s no need to constantly apply patches or worry about server downtime; those are handled by the provider. The ERP software is kept up-to-date with the latest features and best practices automatically. You’ll always be on the current version, benefiting from improvements (like new reporting tools or AI features) without going through a painful upgrade project. This allows your IT staff (if you have any) to focus on strategic tasks rather than system upkeep.
3. Scalability and Flexibility
Cloud ERPs let you scale on demand. If your business grows and you need to add 20 new users or open a new location, you can typically scale up by adjusting your subscription; no new servers or complex reinstallation required. Similarly, if you need more modules or functionality, you can often enable them immediately. This flexibility is ideal for growing companies or seasonal businesses. The system can adapt with you, and you pay only for what you use.
4. Accessibility & Collaboration
A SaaS ERP is accessible 24/7 from anywhere with internet. This greatly supports remote work and multi-site collaboration. Salespeople can update orders from the field on a tablet; managers can review dashboards from home or on a business trip. Everyone is connected to the same real-time data. For example, an inventory manager in the warehouse and a sales manager in the field both see current stock levels and order status in the ERP at the same time, enabling quicker decisions. The result is higher productivity and responsiveness across your team.
5. Security & Reliability
Reputable cloud ERP providers offer enterprise-grade security and uptime that many small businesses could not afford on their own. They have robust data centers with redundancy, backup protocols, and professional security teams monitoring threats around the clock. Data is regularly backed up and often spread across multiple geographies for disaster recovery. In many cases, a cloud solution can reduce risk compared to an under-resourced on-premise setup, provided the vendor has proper certifications. Of course, it’s important to choose a trustworthy provider and follow best practices (like strong user passwords and access controls), but generally, your data is very safe in a modern cloud ERP.
6. Faster Access to Innovation
Cloud ERP systems tend to integrate new technologies more rapidly. Vendors can push out enhancements like AI-powered analytics, machine learning forecasts, or mobile app improvements to all subscribers at once. This means even a small company using a SaaS ERP can leverage cutting-edge features (e.g., AI-assisted financial close, or chatbot customer service integrations) that might have been costly or slow to adopt on a self-hosted system. In a fast-moving tech environment, cloud ERP ensures you’re not left behind with outdated software.
In summary, the cloud model offers significant advantages in cost, convenience, and capabilities. That said, on-premise ERPs can still make sense if you require absolute control or offline availability, it depends on your situation. For most, though, the benefits of cloud ERP make it an appealing choice, especially for small and mid-sized businesses aiming to minimize IT hassles.
Tip: If you have an existing on-prem ERP and aren’t ready to fully replace it, you can often integrate cloud modules or third-party apps to extend its life, a strategy to gradually enjoy cloud benefits without a big bang switch.

Types of ERP Systems
ERP systems are not one-size-fits-all. There are many kinds of ERP solutions designed for different needs. When shopping for ERP, it helps to understand the various ERP system types available in the market. Key ways to categorize ERPs include:
1. By Deployment Model
The three common types are on-premises, cloud, and hybrid ERP. On-premises ERP is installed locally under your control; cloud ERP is provided as SaaS (discussed above); hybrid ERP combines both (for example, a company might keep core finance on-prem but use cloud modules for CRM or analytics). Knowing which deployment model you prefer is a fundamental step in narrowing your options.
2. By Industry or Niche
Some ERPs are general-purpose, while others are built for specific industries. For example, there are specialized ERPs for manufacturing, healthcare, construction, retail, etc. An industry-specific ERP comes with built-in processes and features for that sector (for instance, a real estate ERP might have property management and lease tracking capabilities).
These targeted systems can minimize the need for customization since they offer tailored features for the business type, meaning companies don’t have to integrate many external tools or heavily modify the software to fit their needs. If your industry has unique requirements (like lot tracking in food manufacturing or project billing in construction), you might lean toward a vertical ERP solution. On the other hand, many popular ERPs (SAP, Oracle, Microsoft Dynamics) serve a wide range of industries through configurable modules.
3. By Company Size (SMB vs Enterprise)
ERP vendors often tailor products to different-sized organizations. “Tier 1” ERPs (like SAP S/4HANA or Oracle Fusion) are aimed at large enterprises with thousands of users and very complex processes. They have extensive features, but also higher complexity and cost. SMB (small and mid-size business) ERP solutions (like SAP Business One, Oracle NetSuite, Microsoft Dynamics 365 Business Central, or Odoo) are scaled to mid-market needs, easier to implement, with a focus on affordability and usability for smaller teams.
Choosing an ERP that matches your organizational size ensures you get the functionality you need without excessive complexity or cost. A fast-growing small company might start with a lighter-weight ERP and upgrade tiers as it becomes an enterprise.
4. Proprietary vs Open-Source
Another consideration is the software licensing model. Proprietary ERPs are commercial products from vendors who develop and sell the software (e.g., SAP, Oracle, Microsoft). You typically pay for licenses or subscriptions, and the source code is closed. In contrast, open-source ERP solutions like Odoo or ERPNext provide their source code openly, allowing for greater customization by developers and often lower licensing costs (sometimes free for the base system).
Open-source ERPs can be attractive for those who want maximum flexibility and control over the software’s behavior. You can modify the code to fit unique requirements. They also foster large communities that create add-ons. However, open-source doesn’t mean “no cost”; you still need technical expertise to implement and support it (or a partner like Encloud to do it for you). Decide if your team prefers a well-supported commercial product or is open to an open-source approach for more customization.
5. Modular Suites vs Integrated Systems
Modern ERPs are usually modular (you pick the modules you need). Some vendors offer a full suite of applications under one umbrella, while others allow a more mix-and-match approach. For instance, an all-in-one suite might include every module (financials, CRM, HR, inventory, etc.) that works seamlessly together.
Alternatively, you might use a core ERP for finance and supply chain, but integrate it with a separate CRM or HR system. When evaluating ERP types, consider whether you want a single vendor for all functions or if you plan to integrate multiple specialized systems (which requires strong integration capabilities). In practice, you will be looking at a combination of these factors.
For example, you might seek a cloud-based, SMB-focused, open-source ERP for a manufacturing business; that description would point you toward certain options (like Odoo). Understanding these categories helps you filter the vast ERP landscape down to a shortlist that fits your deployment preference, industry, size, and flexibility needs.
Also Read: Best Zoho CRM Development Company
Famous ERP Systems & Examples
The ERP market has several well-established players that are considered the top or famous ERP solutions worldwide. It’s useful to know some of these names as examples of ERP systems when doing your research. Here are a few notable ERP products:
1. Odoo ERP
Among newer and alternative options, Odoo is an open-source ERP platform that has gained huge popularity, particularly with small and mid-sized businesses. Odoo’s modular design (with apps for every business function) and affordable cost, it even has a free Community edition, make it an attractive example ERP solution for companies that want flexibility. It can be deployed on-premise or in the cloud and is highly customizable (a big plus if you have unique processes).
Encloud Solutions specializes in Odoo implementations because of Odoo’s adaptability across industries. While Odoo might not be as famous historically as SAP or Oracle, it’s a rising star and worth considering if you want a modern, customizable ERP without breaking the bank.
2. SAP (Systems Applications and Products in Data Processing)
SAP is one of the original pioneers of ERP software and remains a market leader. Their flagship product, SAP S/4HANA, is used by many large enterprises globally. SAP ERP is known for its depth in manufacturing, supply chain, and finance features. (Fun fact: SAP itself is a company name that has become synonymous with ERP in some circles, but remember, SAP is the vendor, and ERP is the category of software. SAP’s ERP is one example ERP system among many.) SAP also offers SAP Business One for small/midsize companies.
3. Oracle (Fusion ERP / NetSuite)
Oracle provides multiple ERP solutions. Oracle Fusion Cloud ERP is a comprehensive suite for large organizations, while Oracle NetSuite (which Oracle acquired) is a very popular cloud ERP for small and mid-sized businesses. NetSuite was one of the first pure SaaS ERPs and is widely used for its strong financials and multi-subsidiary management capabilities. Oracle’s ERPs are known for robust databases and powerful reporting, and Oracle has been a leader in pushing cloud-based ERP adoption.
4. Microsoft Dynamics 365
Microsoft’s ERP offerings (Dynamics 365 Finance, Supply Chain, and Business Central for SMBs) leverage the familiar Microsoft ecosystem. Dynamics 365 Business Central is a common choice for small and growing businesses, integrating nicely with Office 365 and offering cloud deployment. Microsoft’s ERPs are praised for user-friendly interfaces and strong support for things like retail and distribution. As a famous ERP suite, Dynamics competes head-to-head with SAP and Oracle in many industries.
5. Sage & Infor
Sage offers ERP solutions like Sage X3 and Sage Intacct, especially strong in accounting and financial management for mid-market companies. Infor provides industry-specific cloud ERPs (Infor CloudSuite) targeted at verticals like manufacturing, healthcare, and fashion. These are also well-known in the ERP space, albeit catering to specific niches.
These are just a few examples. Other famous ERP systems include Epicor, Acumatica, IFS, Workday (focused on HCM and finance), Unit4 (popular in services and education), and Zoho ERP offerings, among others. Each ERP system has its strengths and ideal use cases.
For instance, SAP and Oracle often serve Fortune 500 enterprises with complex global operations; Microsoft Dynamics works well for many mid-market firms; Odoo can be tailored to small businesses or specific verticals with ease. When researching solutions, consider your industry peers. What do companies of similar size and sector use? That can give you a clue to which ERP might suit you.
Remember, the best ERP for you is not necessarily the one with the biggest name, but the one that fits your business requirements the closest. In the next section, we’ll discuss how to buy an ERP system and what steps to take to ensure you choose the right solution out of these many examples.

How to Buy an ERP System
Now that you understand the landscape, let’s get into how to buy ERP effectively. Purchasing an ERP system involves more than just picking software; it’s about finding a solution that aligns with your business processes and setting it up for success. Here’s a step-by-step guide to help you through the ERP buying process:
1. Identify Your Needs & Goals
Start by documenting what you need from an ERP. Engage people from each department, for example, have your inventory managers list requirements for warehouse management, and sales managers outline what they need for order processing and CRM integration. Determine the pain points in your current process (e.g., duplicate data entry, lack of real-time reporting) and the must-have features (inventory tracking, financial consolidation, production planning, etc.).
Also consider your future goals: Are you planning to expand to e-commerce or new locations? Any industry-specific needs (like project management for real estate or compliance tracking for a solar energy business)? Creating a detailed checklist of requirements and objectives will serve as your blueprint when evaluating ERP options.
2. Decide on Cloud vs On-Premise Early
As discussed, one of the first strategic choices is the deployment model. Consider your IT capabilities, budget, and company policies. If you have minimal IT support and want quick setup and accessibility, an ERP system SaaS (cloud ERP) model is likely the best fit. If you operate in an area with poor internet or have strict data residency rules, on-premises might be required. For most, the cloud will be appealing for the reasons we covered (lower cost, automatic updates, remote access).
Make sure stakeholders understand the trade-offs of ERP vs cloud ERP. This decision will immediately narrow down your vendor list (since some ERPs are cloud-only, like NetSuite, while others offer both options). Don’t forget to factor in long-term costs: cloud is pay-as-you-go, whereas on-prem has a bigger upfront cost but potentially lower recurring fees. Tip: Unless you have a compelling reason to host the system yourself, modern cloud ERP offerings are very mature and often the faster route to value.
3. Set a Budget & ROI Expectation
Determine how much you are willing to invest in an ERP, including not just software fees but also implementation services, training, and ongoing support. ERP costs can vary widely, from affordable subscriptions of ~$20/user/month for some cloud ERPs to millions of dollars for large enterprise projects. Knowing your budget range will help you target the right tier of solutions. Also, consider the ROI (return on investment). What efficiency gains or cost savings do you anticipate?
For example, if an ERP can automate tasks and reduce inventory holding costs, that translates to real savings. Many companies justify the cost of ERP by the improvements in productivity and decision-making it brings. Having an ROI mindset will help you make a business case for the purchase and choose a solution that delivers value. Be wary of over-customizing or buying modules you won’t use; focus on core needs first to keep costs manageable.
4. Research & Shortlist ERP Vendors
Armed with your requirements and budget, you can now evaluate specific ERP products. Look for software that matches your needs in terms of industry focus, company size, and features. There are many resources online (analyst reports, user reviews, case studies) that compare ERP vendors. Create a shortlist of perhaps 3–5 ERPs to investigate in depth.
For each, consider: Does it have all the modules you need? Is it known to serve companies in your industry? Is it cloud-based (if you decided on cloud)? How is the user interface (modern and easy or old and clunky)? Also, take note of the pricing structure and whether it’s within budget. If you’re a small business, you might focus on simpler solutions tailored to SMBs.
See our in-depth best ERP for small companies guide for some recommendations and cost comparisons. Likewise, if you’re in a niche industry, check if there’s a specialized ERP or a particular vendor with expertise in that area. Peer referrals and independent software review sites can be helpful to gauge satisfaction levels. The goal of this step is to narrow down to a top 2 or 3 contenders that seem like a good fit.
5. Demo the Software & Ask Questions
Never buy an ERP without seeing it in action. Arrange demos with the vendors or their implementation partners. Use your own business scenarios during the demo if possible, for example, ask them to show how the system would handle a sales order through to inventory deduction and invoice generation, or how the ERP and SaaS platform integrates with a CRM if that’s important to you.
Gather feedback from your team members who attend the demos; they will often notice if the software seems intuitive (or not) for their daily work. During this phase, ask about customization and integration capabilities. If you have existing systems (like an e-commerce site or a specific CRM), can the ERP connect to them easily? Vendors should be able to speak to APIs or integration tools. This is also the time to inquire about support, training, and implementation services.
Some vendors will connect you with an implementation partner firm (like Encloud Solutions, if you were evaluating Odoo, for instance). Get clarity on what resources are provided for getting the ERP up and running. It’s wise to request a trial or sandbox environment if available, so your team can test the interface hands-on. Treat the demo like a test drive; it’s your chance to see if the ERP truly fits before you commit.
6. Plan for Customization & Integration
No ERP will fit your business perfectly out of the box, especially if you have unique processes. Determine what (if any) customizations you’ll need. This could range from simple tweaks (adding a custom field or report) to more significant changes (e.g., customizing workflows or developing a module for a special process).
Understand from the vendor how customization works, whether it can be done via configurations, or does it requires coding? Modern systems like Odoo or Dynamics allow a lot of configuration without coding, whereas others might need developer work for changes. Consider who will do this work: do you have IT developers in-house, or will you rely on a partner? Also, make an integration plan. List the other software your business uses (CRM, e-commerce, POS, legacy databases, etc.) and ensure your ERP can connect to them.
Smooth data flow between systems is crucial; for example, you might want your website orders to flow into the ERP automatically or your ERP to push financial data to a budgeting tool. Many ERPs offer integration modules or APIs for this purpose. Encloud Solutions provides ERP integration services to help companies link their ERP with e-commerce platforms (Shopify, WooCommerce, Amazon), payment systems, third-party logistics, and more.
Proper integration eliminates data silos and double-entry, maximizing the ERP’s value. Include these customizations and integrations in your project scope and budget. It’s better to plan for them up front than to be surprised later. (Note: Avoid over-customizing in phase 1. Start with essential tweaks that give you a competitive advantage, but try to use standard ERP features where possible; this keeps the system simpler and upgrade-friendly.)
7. Choose a Trusted Implementation Partner
Buying the software is just one part; implementing it successfully is equally critical. Many ERP failures stem from poor implementation rather than the software itself. Unless you have a skilled internal IT team that has done ERP projects before, it’s highly recommended to work with an experienced ERP consultant or implementation partner. These are firms (or individuals) that specialize in deploying the ERP, configuring it to your needs, migrating your data from old systems, and training your users.
Encloud Solutions, for example, is an official Odoo partner and has a track record of end-to-end ERP implementation and customization. A good partner will understand your industry, help tailor the system (they can build custom features or reports if needed), and ensure best practices are followed so that you get a smooth go-live. They also provide support after launch, which is invaluable for troubleshooting and continuous improvement. When selecting a partner, consider their expertise (do they know your chosen ERP and industry?), their services (do they offer training, support, integration, etc.?), and client references or case studies.
Essentially, the partner should feel like an extension of your team, guiding you through this transformation. The right partner will make your ERP project faster, less risky, and more aligned with your business objectives. Don’t hesitate to ask potential partners about their implementation methodology and how they manage timelines and budgets. ERP implementation is a collaborative process; you’ll need to allocate internal resources, too, but with experts leading the way, you greatly increase the chances of success.
By following these steps, you’ll be well on your way to purchasing an ERP system that fits your company. It’s an educational journey: from understanding your needs, surveying the ERP landscape, to finally executing the deployment. Always keep the end goal in sight, a unified system that empowers your business, and you’ll be able to justify the effort and investment.
Also Read: Zoho Field Service Software That Integrates with QuickBooks
Remember: an ERP is not just software, it’s a strategic business decision. Treat it as such by involving stakeholders, doing thorough homework, and leveraging expertise where needed. The payoff can be huge; companies often see improved efficiency, better decision-making, and scalability once a good ERP is in place. In the next section, we’ll highlight why Encloud Solutions could be the ideal partner in this journey.

Encloud Solutions: Your ERP Partner
Implementing ERP can be challenging, but you don’t have to do it alone. Encloud Solutions is a professional IT consulting firm that specializes in custom CRM and ERP solutions. From the initial selection process through integration, training, and ongoing support, our team assists businesses every step of the way. We’ve helped companies of all sizes modernize their operations with ERP, empowering them to streamline workflows, eliminate data silos, and achieve faster growth.
Encloud Solutions is known for its expertise in Odoo ERP, a flexible open-source platform. (We are an official Odoo Gold Partner, which means we are certified to implement and fully customize Odoo for clients’ unique needs.) However, our services are not limited to one product; we always start by understanding your requirements and then craft a tailored solution. Whether you’re in manufacturing, distribution, real estate, solar energy, retail, or any other sector, we can adapt the ERP to fit your industry-specific processes.
Our team has developed industry modules (for example, real estate property management features, or solar project tracking capabilities) and performed countless integrations between ERP and other software. If you have legacy systems or specialized applications, we ensure your new ERP will talk to them seamlessly (via our ERP integration services). Customization is our strength; we say “yes” to customizing the ERP so that it molds around your business, rather than forcing you to change your workflows. Encloud’s consultants take pride in delivering an ERP that feels just right for the client.
Choosing Encloud Solutions means choosing a partner committed to your long-term success. We don’t just do the installation and vanish; we provide training to your users, support after go-live, and continuous improvement advice as your business evolves. Our goal is to maximize your ROI from the ERP investment by ensuring high user adoption and uncovering efficiency gains. In short, we handle the technical heavy lifting and guidance, so you can focus on running your business with the new system.
Ready to take the next step? If you’re considering an ERP implementation or upgrade, contact Encloud Solutions for a free consultation. We’ll discuss your goals and show you how a tailored ERP solution can transform your operations. With Encloud as your partner, you can confidently move forward in your ERP journey, knowing you have the best support to achieve a successful outcome.

FAQs
What is ERP and SaaS?
ERP (Enterprise Resource Planning) is a type of business software that manages and integrates a company’s core processes (finance, inventory, sales, HR, etc.) in one system. SaaS (Software as a Service) is a delivery model for software where you access it over the internet on a subscription basis, rather than installing it on your own servers. When we talk about ERP and SaaS together, we’re usually referring to cloud-based ERP solutions provided as a service.
What does ERP stand for in SaaS?
In a SaaS context, ERP stands for Enterprise Resource Planning, the same as in any context. The term doesn’t change; ERP always means the integrated management of key business processes, facilitated by software. So, what ERP stands for in SaaS is still enterprise resource planning.
Is ERP an IT system?
Yes, ERP is an IT system in the sense that it’s software used to run business operations. More specifically, ERP is a comprehensive business application (or suite of applications) that falls under a company’s information technology infrastructure. When you implement an ERP, you are deploying a major IT system that users will interact with daily for tasks like entering orders, posting invoices, or running reports.
What do you mean by ERP?
When we talk about ERP, we mean a software solution that enterprise organizations use to plan and manage resources across the company efficiently. The term Enterprise Resource Planning basically implies that the software helps plan and utilize all the resources of an enterprise, be it human resources, financial resources, materials, or even customer relationships.
What is ERP vs CRM?
ERP and CRM are both important business software, but they focus on different areas. ERP (Enterprise Resource Planning) is like the backbone that runs internal processes; it’s about internal efficiency and integrating back-office functions (financials, supply chain, production, HR, etc.). CRM (Customer Relationship Management) is more about the front office; it’s a system to manage interactions with customers and prospects, focusing on sales, marketing, and customer service.
Best Zoho CRM Development Company 2025: Encloud Solutions
Zoho CRM has become a market-leading cloud CRM platform used by over 700,000 businesses across 150+ countries. It offers a 360° view of your customer data (sales, marketing, and support) in one place, making it easy to track leads, contacts, and deals. In 2025, with global CRM spending projected to exceed $114.4B by 2027, businesses need agile, scalable CRM solutions. Zoho CRM fits this need by combining user-friendly dashboards, advanced analytics, and AI-driven insights. If you’re ready to streamline your business with Zoho CRM, contact us today through the form below.
Why Choose Zoho CRM for Your Business
At Encloud Solutions, Zoho CRM development is our core expertise. As a Zoho partner, we help you leverage these features fully. Our clients use Zoho CRM to manage sales pipelines, run marketing campaigns, and deliver top-notch support. Get in touch with our team to learn how Zoho CRM can work for your business. Key advantages of Zoho CRM include:
1. 360° Customer View
All customer interactions (emails, calls, social media, support tickets) are stored in one system. Everyone on your team sees the latest info.
2. Customizable Modules
Tailor fields, layouts, and pipelines to match your processes. Build only the modules you need, so the CRM works the way you do.
3. Seamless Integrations
Built-in connectors (Google Workspace, Microsoft 365, MailChimp, etc.) keep data flowing automatically. No more manual uploads – your apps all speak to each other.
4. Powerful Automation
Workflows, blueprints, and macros eliminate repetitive tasks. Studies show CRM automation can boost productivity by ~30%, letting sales representativess focus on closing deals instead of paperwork.
By choosing Zoho CRM, you get a future-proof platform that grows with your business – backed by expert support from Encloud Solutions. Reach out through our contact form to start your Zoho CRM journey today.

Zoho CRM Development Services at Encloud Solutions
For businesses looking for a skilled developer Zoho CRM, our team is ready to help. Encloud Solutions is a certified Zoho CRM developer company delivering custom Zoho CRM development and implementations. Our experts help companies set up, integrate, and customize Zoho CRM to fit their unique processes. We handle everything from data migration and user training to Zoho CRM setup and customization, ensuring your CRM goes live quickly and smoothly. Fill out our contact form to discuss your CRM setup or customization needs.
Also Read: Zoho Field Service Software That Integrates with QuickBooks
Why custom development? Off-the-shelf CRMs often have features you don’t need and workflows that don’t match your business. A tailored Zoho CRM adds only the functionality you want. In practice, companies with custom CRM solutions often see 20–30% higher productivity and a strong ROI (roughly $8.71 returned for every $1 invested). Many of our clients recoup their implementation costs within a year thanks to streamlined operations and improved adoption. Talk to our experts about how custom Zoho CRM development can improve your ROI – just send us a quick message using the contact form. Our Zoho CRM services include:
1. Custom Development
We build new modules, custom fields, and user interfaces so the CRM matches your industry and business needs.
2. Expert Guidance
Certified Zoho CRM professionals work with your team to design the right solution. We analyze your sales and support processes and configure Zoho CRM accordingly.
3. Integrations
We connect Zoho CRM to your existing systems (ERP, email marketing, e-commerce, and more). For example, we can synchronize inventory from your ERP, so product levels update in real-time and capture leads from your website forms directly into Zoho.
4. Implementation & Support
From initial planning to end-user training, we provide end-to-end service. After go-live, we offer ongoing support. Whenever you need a Zoho CRM developer to add a feature or fix an issue, we’re here to help.
5. Zoho CRM Customizations
We cover all Zoho CRM customizations (also spelled Zoho CRM customisation). This includes advanced tweaks to modules, data layouts, and automation rules, so the system evolves as your business does.
By partnering with Encloud Solutions, you ensure your Zoho CRM exactly fits your needs, no compromises, no unused features. Contact us to get personalized guidance from our certified Zoho CRM developers.

Customizing and Extending Zoho CRM
Every business has unique workflows. With customizing Zoho CRM, Encloud Solutions makes the CRM conform to you. We create Zoho CRM custom modules and fields to capture the data you care about. For example, if you run a solar-energy company, we might add a module for Installations and link it to customer accounts. We then customize Zoho CRM so sales reps see only relevant fields, which makes the interface intuitive. If you want a CRM that works exactly the way your business does, get in touch with us today. Customization highlights:
1. Custom Modules & Fields
Design new modules or extend existing ones. Use lookup fields to relate data (e.g., link a Warranty Record to a product and customer).
2. Workflows & Blueprints
Automate tasks like lead assignment, email notifications, and approvals. For example, automatically send a follow-up email when a deal stage changes.
3. Custom Scripting
Using Zoho’s low-code Deluge or Java SDK, we implement advanced logic. A key example is Zoho CRM get emails under custom modules. Incoming emails can be automatically attached to the correct record based on content.
4. Data Transfers
Handle complex cases such as Zoho CRM transferring linked attachments to another module. Suppose an invoice is created in one module; our code can copy its attachment link to a related project record automatically.
5. Advanced Relationships
Link records flexibly. We can link a meeting to multiple accounts (if one meeting involves several clients) or relate custom calendar events to contacts.
Also Read: ERP for Small Companies
By focusing on how to customize Zoho CRM precisely, we help teams adopt the system quickly. Tailored CRMs reduce manual work and errors – one study noted ~20–30% productivity gains with custom software. A custom Zoho CRM keeps your team efficient and data clean. Reach out now to find out how we can tailor Zoho CRM for your organization.

Zoho CRM Integration and Automation
Zoho CRM really excels when connected to the rest of your tech stack. We are experts in email integration with Zoho CRM, so you never lose track of conversations. For example:
1. Zoho CRM email integration
Connect your Gmail or Office 365 account to Zoho CRM. With the built-in Zoho mail client, all sent/received emails automatically log to the correct contacts and leads. This way, every customer email is captured without extra effort.
2. Zoho CRM and Zoho Calendar integration
Sync meetings and events from Google Calendar or Outlook with Zoho CRM. A demo scheduled in Google Calendar will appear on the related contact’s timeline in CRM, keeping sales appointments in one place.
3. Zoho CRM Google Meet integration
Automatically attach Google Meet links and recordings to CRM events. When a virtual meeting is created, the link is stored in Zoho so you can easily follow up with notes.
4. How to import leads in Zoho CRM
We help onboard new leads from spreadsheets or other sources. Imported leads retain their source tags and campaign data, so your marketing funnel stays intact.
5. Zoho CRM integration with Outlook
Use Zoho’s Outlook plugin to access CRM contacts and log Outlook emails or tasks to Zoho CRM. Your sales team can work in Outlook while Zoho CRM updates in the background.
Beyond email and calendar, we connect Zoho CRM to virtually any system. Whether it’s adding telephony integration (RingCentral/Twilio) so calls auto-log, or syncing e-commerce data so orders appear in CRM, we make it happen. These automations pay off: studies find companies using CRM automation see up to a 245% increase in revenue and 23% lower lead acquisition costs, since nothing falls through the cracks. Fill out our contact form to integrate Zoho CRM seamlessly with your existing systems.

Zoho CRM Dashboards and Analytics
Getting insights from your CRM data is vital. Zoho CRM’s dashboards and reports let you visualize performance at a glance. Encloud configures dashboards tailored to your KPIs. For example:
1. Custom Dashboards
Show pipeline summaries, conversion rates, and team targets on one screen. Give each user a personalized view (sales rep vs. manager).
2. Real-time Reports
Drill down by region, product line, or campaign. Spot trends and answer questions on the fly (e.g., “Which sales rep leads are converting best?”).
3. Forecasting & AI
Zoho’s Zia can predict sales trends and alert you to at-risk deals. Using AI-powered forecasts, managers know which quotas may be in danger before it’s too late.
4. Automated Analytics
Schedule reports to email your leadership team weekly. This saves time and ensures strategic decisions are data-driven.
By tailoring Zoho CRM dashboards to your business, you unlock actionable intelligence. Companies leveraging CRM analytics have seen marketing costs drop ~23% and conversion rates significantly improve. With the right reports, you’ll spot issues early and seize opportunities faster. Talk to our team to design dashboards and reports that drive better decisions – use the contact form to get started.

Zoho CRM Pricing and Editions (2025)
Zoho CRM offers editions that scale with your needs. Here’s a quick comparison (annual subscription, per-user pricing):
| Edition | Price (User/Month) | Highlights |
| Free (Standard) | Free for 3 users | Basic lead/contact/deal tracking, tasks, and email templates |
| Standard | $14 | All Free + mass email campaigns, custom modules, workflows |
| Professional | $23 | Standard + Blueprint automation, CPQ/quotes, inventory mgmt |
| Enterprise | $40 | Professional + Zia AI assistant, territory management, portals |
| Ultimate | $52 | Enterprise + enhanced limits, custom AI/ML platform, analytics |
(All prices from Zoho’s official edition comparison. Local taxes may apply.) Each higher edition includes all features of the lower tier, plus advanced tools for growth. Even the entry-level Standard gives you a robust CRM. And since you only pay for users you need, Zoho CRM projects often pay back quickly – our clients typically achieve ~55% ROI in the first year due to efficiency gains and increased sales. If you’re not sure which Zoho CRM edition fits your company, contact us for a free consultation.
Also Read: ERP vs Cloud ERP
Partnering with Encloud Solutions
Investing in an experienced Zoho partner pays dividends. Encloud Solutions not only implements Zoho CRM, but becomes your ongoing advisor. Our certified developers and consultants ensure the system aligns with your strategy. We document your unique workflows, train your staff, and drive high user adoption (which is critical for success). Reach out through our contact form to partner with our Zoho-certified team today.
As Zoho releases new features, we keep you updated. When Google Meet or email tools update, we’ll integrate them into your CRM. This means you always benefit from Zoho’s latest capabilities without extra hassle. Stay ahead with expert Zoho CRM support – contact us anytime to learn how.
In short, our expertise means fewer headaches for you. We turn Zoho CRM into your competitive advantage, delivering stronger growth and efficiency. Ready to get started? Fill out the contact form and let’s build your perfect Zoho CRM.

Frequently Asked Questions
What language is Zoho CRM developed in?
Zoho CRM is primarily built using Java. Java’s platform independence means the CRM can run on any device or OS. The Zoho CRM interface uses web technologies (HTML, CSS, JavaScript) to provide a responsive user experience.
What is Zoho CRM used for?
Zoho CRM is used to manage customer relationships and sales pipelines. It stores leads, contacts, companies (accounts), and deals/opportunities. Sales teams use it to track deal progress; marketers use it to segment and email customers; support teams track tickets or customer history. In essence, it centralizes all customer and sales data (contacts, communications, transactions) so teams can collaborate effectively.
Does Zoho have SEO?
Zoho CRM itself isn’t an SEO tool, but the Zoho ecosystem includes SEO features. For example, Zoho Sites is a website builder with built-in SEO optimization (sitemaps, meta tags). Zoho Commerce also provides SEO tools for online stores. Zoho’s marketing suite (Marketing Plus) supports SEO campaign management. So yes, Zoho offers SEO capabilities through its web and marketing products.
What is the architecture of Zoho CRM?
Zoho CRM is a multi-tenant cloud application. This means multiple companies share the same software infrastructure securely, while their data remains isolated. It runs on distributed server clusters that auto-scale with demand. The system provides real-time synchronization: when a user updates a record, changes propagate instantly. Zoho handles all backend maintenance (servers, databases), delivering a reliable, always-on CRM service.
What technology does Zoho use?
Zoho’s core technology stack centers on Java for its backend services, along with enterprise databases and cloud infrastructure. Zoho provides RESTful APIs and SDKs (including Java and Deluge) for integration. The front end uses modern web frameworks. In summary, Zoho combines enterprise-grade tech (Java, cloud servers) with flexible developer tools to deliver scalable CRM solutions.
What is the structure of a CRM?
Most CRMs have a relational, modular structure. Core modules include Leads, Contacts, Accounts (Companies), and Deals/Opportunities. These tables link together: for example, each Contact belongs to an Account, and leads convert into deals. Zoho CRM’s documentation lists Leads, Contacts, Accounts, and Deals as core modules, plus supporting modules like Activities, Products, and Campaigns. Essentially, data flows through these linked tables – that modular design is common to all CRMs, allowing you to extend with custom modules as needed.
What is Zoho CRM’s Dashboard?
Zoho CRM provides customizable dashboards where you can display charts and metrics (e.g., pipeline value, sales cycle length). You can drag-and-drop dashboard components to see key KPIs at a glance. Managers often set up dashboards for sales targets, while reps see their own lead stats. Dashboards update in real-time with your CRM data, helping teams stay on track and make data-driven decisions.
ERP for Small Companies: 2025 Guide to ERP Solutions & Costs
Small businesses today face growing complexity in operations, and ERP for small companies has become increasingly critical. As noted by experts, modern ERP systems centralize core operations, which combine accounting, inventory, sales, and HR functions in one platform.
This integration is a game-changer: one guide calls ERP a comprehensive tool that unifies scattered data and automates processes for small teams. With about 65% of small businesses already using ERP to manage and scale their operations, it’s clear that even smaller firms are benefiting from these affordable, cloud-based solutions.
Also Read: ERP vs Cloud ERP
Why Small Businesses Need ERP?
Small companies often start with basic accounting or spreadsheets, but these patchwork solutions can’t keep up as sales, inventory, and projects grow. ERP (Enterprise Resource Planning) fills the gap. It automates repetitive tasks and makes data available in real time across departments.
For example, a retail startup using small business ERP software can automate order processing and inventory tracking, which handles higher sales volumes without hiring extra staff. Centralized ERP data also means managers get instant insights that enable quick, data-driven decisions. In short, ERP acts as a central hub for vital business information, streamlining operations and eliminating costly errors.
Key Point: ERP software is not just for large enterprises anymore. Scaled-down, cloud-based ERPs let small businesses unify finance, inventory, CRM, and more at an affordable price.
Key Benefits of ERP for Small Companies
Implementing ERP for small companies brings many advantages. Below are some of the most important benefits:
1. Improved Efficiency
ERP automates workflows so teams spend less time on manual data entry. This boosts productivity. For example, clients often see 15–20 fewer hours of weekly data entry after an ERP goes live.
2. Centralized Data & Insights
All departments use the same system, giving one real-time single source of truth. Owners and managers get immediate visibility into inventory levels, sales orders, and financial performance. This enables faster, informed decisions with powerful dashboards.
3. Scalability
The right ERP grows with your business. Most small ERP solutions are modular; you can start with core functions and add more modules (e.g., manufacturing, POS, ecommerce) as needed. Cloud-based ERP typically allows new users and features to be added quickly without major re-implementation.
4. Cost Savings
While ERP requires investment, it often pays off by reducing waste and errors. A study notes that companies see 20–30% less inventory waste after ERP, plus faster invoice processing. Centralizing processes also means fewer duplicate software subscriptions and less maintenance overhead.
5. Better Customer Service
Integrated CRM and sales features help track leads and orders from one place. As one guide explains, a unified system helps prevent costly errors and improve customer service by ensuring sales and inventory are in sync.
ERP for small companies thus helps businesses handle growth and complexity without ballooning headcount. It brings enterprise-grade practices (automated bookkeeping, compliance checks, BI reporting) into the reach of startups and SMBs.
Essential Features of Small Business ERP
Not all ERP systems are created equal. For a small company, the right ERP should focus on core needs with a simple interface. Key features to look for include:
1. Financial Management
Beyond basic bookkeeping, strong ERP software automates accounts payable/receivable (AR/AP), handles multi-currency and tax compliance, and provides easy bank reconciliations. You should get real-time financial reporting and audit trails without manual spreadsheet juggling.
2. Inventory and Supply Chain
Real-time inventory tracking with multi-warehouse support is a must. The system should prevent stockouts (via reorder alerts) and optimize locations (e.g., bin tracking). Basic supply-chain tools (automated purchase orders, vendor management, demand forecasts) help small businesses cut carrying costs and keep stock healthy.
3. Customer Management
Even a basic CRM is valuable. An SMB ERP should include contacts, sales pipelines, and order history so sales reps and managers see all client interactions. Integrating sales orders with inventory and invoicing (all within ERP) helps prevent costly errors and improve customer service.
4. Human Resources & Payroll
At minimum, the ERP should track employee records, time/work hours, and payroll basics (taxes, benefits). This keeps all HR data in one place and can automate payroll calculations. Even a rudimentary HR module adds value by reducing manual error.
5. Reporting & BI
Look for customizable dashboards and key performance indicator reports. Small teams need at-a-glance analytics without building complex reports from scratch. The ERP should let you see KPIs (sales pipeline, cash flow, inventory turns, etc.) on demand, on any device.
6. Mobile Access
Today, your team expects mobile-friendly access. A small ERP should offer web or app interfaces so managers and staff can check inventory levels, approve invoices, or view orders on tablets and smartphones. Remote access means faster approvals and quicker response times.
These core functions drive daily efficiency and give small businesses an immediate return on investment. Once those basics are in place, you can consider advanced add-ons (e-commerce integration, project modules, IoT, AI tools) as needed. But as one expert advises, master the core features before over-investing in extras.
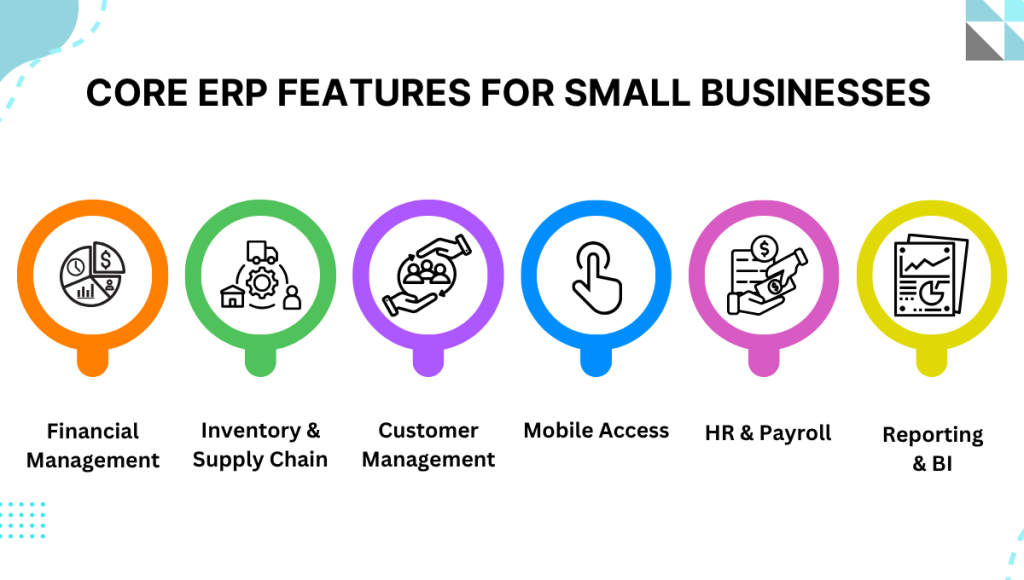
Top ERP Systems for Small & Midsize Businesses
What are the best software choices? Many ERP vendors now target SMBs. Below are some widely-recommended solutions (with internal targets):
1. Odoo ERP
An open-source suite that is highly scalable and cost-effective. Odoo’s modular apps cover everything from CRM and accounting to inventory and e-commerce. Its Community edition is free (no license fees), while Enterprise edition adds advanced features and support. Odoo’s open design means you only pay for what you use. (Encloud Solutions specializes in custom Odoo ERP software and has helped thousands of businesses deploy it.)
2. Microsoft Dynamics 365 Business Central
A popular cloud ERP for SMBs, often cited as a top ERP system for small business. It includes finance, inventory, sales, and project modules. D365 Business Central tightly integrates with Office 365 apps, which many growing firms like. Licensing is subscription-based (roughly ~$70+/user/month). It’s an excellent choice for companies already in the Microsoft ecosystem.
3. SAP Business One
Designed specifically for small and mid-sized companies, SAP B1 offers comprehensive ERP features (financials, sales, CRM, inventory) in one package. It can be deployed on-premise or in the cloud. Because it’s enterprise-class, the one-time license is higher (around $1,350–$3,200 per user), though volume discounts may apply. SAP B1 is known for depth of features and strong reporting.
4. Oracle NetSuite
A true cloud-based ERP, NetSuite works well for fast-growing businesses and subsidiaries. It combines ERP, accounting, and CRM in one. Pricing is per user/month (often higher end) and depends on chosen modules. NetSuite stands out for multi-currency and multi-subsidiary management, which is great for companies with global ambitions.
5. Sage Intacct, Acumatica, or Others
Other contenders include Sage’s SMB ERPs (especially strong in accounting) and Acumatica (a growing cloud ERP focused on ease-of-use). Each of these has merits depending on your industry research, which is best ERP for midsize companies in your sector.
Figure: An ERP dashboard (Odoo) showing integrated business functions. Modern SMB ERP software like this centralizes processes in one interface.
The best ERP for your company ultimately depends on your needs and budget. Experts recommend evaluating options like Odoo, Business Central, SAP B1, and industry-specific systems side-by-side. When comparing systems, consider factors such as deployment model, customization, user interface, and integration capabilities.
Also Read: ERP Integration Services
Below is a brief comparison of popular ERP systems by price and focus:
| ERP Solution | Typical Pricing | Key Strengths |
| Odoo ERP (Open-Source) | $0–$25 per user/month | Modular (CRM, Accounting, Inventory, etc.); highly customizable; large app ecosystem |
| Microsoft D365 BC | $70+ per user/month | SMB-focused; strong Office integration; AI/BI tools; scalable in Azure cloud |
| SAP Business One | $1,357–$3,213 per user (one-time) | Rich SMB ERP feature set; industry vertical support; on-premise or cloud; robust analytics |
| Oracle NetSuite | Cloud subscription (per-user) | All-in-one global cloud ERP; strong multi-entity accounting; robust ecommerce/CRM |
| Acumatica | Cloud subscription (per-user) | Flexible deployment (cloud/on-prem); strong finance; built for future growth |
Cost of ERP for Small Business
Cost of ERP system for small business can vary widely. Key factors include the number of users, deployment model, customization level, and vendor. Here are some general guidelines:
1. License or Subscription Fees:
Cloud ERP is usually subscription-based. Experts note that monthly per-user costs often run $40–200 for small businesses. For example, Dynamics 365 BC starts around $70/user/month. Odoo Community is free, while Odoo Enterprise is about $20–25/user/month. On-premise ERP typically requires buying a perpetual license (e.g., SAP B1’s professional license is ~$3,213/user) plus annual maintenance (often ~18–22% of license).
2. Implementation & Setup
Beyond software fees, there’s cost to implement an ERP. A rule of thumb (from industry data) is that small businesses invest $5,000–$25,000 in implementation and training. This covers configuration, data migration, and user training. Complex customizations or integrations can raise this cost.
3. Ongoing Maintenance
If on-premise, expect server and IT maintenance. Even cloud ERP has support fees. Many vendors charge an annual support fee (~18% of license) or include it in subscription. Factor in updates, hosting, and any add-on modules you need.
4. Total Cost of Ownership
For decision-making, consider the 5-year total cost. One study shows Odoo’s five-year TCO is roughly 40–60% lower than comparable SAP or Microsoft solutions due to lower licensing and implementation effort.
Ultimately, calculate both upfront and recurring costs. Small ERP deployments can be quite cost-effective; for many, the efficiency gains and growth support outweigh the initial expense. Consider cloud ERP to minimize infrastructure costs, as one guide recommends, cloud deployments have minimal upfront costs and fast ROI.

Choosing the Right ERP & Deployment
With so many options, how do you select the right ERP? Start by documenting your business needs, which modules you must have (like inventory, accounting, or CRM) and which can wait. Encloud Solutions’ experts suggest evaluating: required features, project timeline, IT resources, and budget. For example, ask vendors: What are all first-year costs, including add-ons and support?. Also plan for growth: choose a system that can scale from your current users to several times more without expensive rework.
1. Cloud vs On-Premise
Today, most small businesses choose cloud ERP for lower IT burden. Cloud ERP usually means lower upfront cost and includes automatic updates. On-premise gives you data control but requires hardware and IT staff. Unless you have strict compliance needs, cloud ERP is often more practical for small firms.
2. Customization & Integration
Standard ERP features might meet 80% of needs, but you may need some custom tweaks or integrations. For example, if you use an e-commerce or POS system, ensure your ERP can integrate with it. Encloud Solutions provides ERP integration services to connect ERP software with other business tools. Their Odoo integration service includes connectors for Shopify, WooCommerce, Amazon, QuickBooks, and more, which eliminates manual data entry between systems.
3. Vendor and Support
Because small businesses often have limited IT support, choose a vendor (or implementation partner) that offers strong service. Encloud Solutions, for example, specializes in custom ERP solutions and provides end-to-end implementation, training, and ongoing support. They are an Odoo Gold partner, meaning they can both implement and fully customize Odoo ERP for your industry.
Industry-Specific Considerations
Some industries have unique needs that ERP can address. For instance, real estate companies benefit from specialized features like property portfolio management, lease booking, and project scheduling. Encloud Solutions has a dedicated Real Estate ERP solution that integrates accounting, CRM, and construction project tracking in one system. (Learn more in our Real Estate ERP Software guide.) Similarly, solar and construction companies might need modules for fixed assets, inventory of parts, job costing, and regulatory compliance. Many modern ERPs (especially flexible ones like Odoo) allow adding or customizing modules for these sectors.
Even if your industry isn’t listed, the right SMB ERP can be adapted. A key advantage of solutions like Odoo is their modular design; dozens of industry apps exist (manufacturing, service, healthcare, etc.). A consultant like Encloud can tailor the ERP to fit your business. They emphasize a tailored ERP architecture built around your workflows, rather than forcing your company to fit generic software.
Also Read: Best Zoho CRM Development Company
Encloud Solutions: Your ERP Partner
Encloud Solutions empowers businesses with custom CRM and ERP solutions. Our experts guide small companies through every step of ERP adoption, from selection and integration to training and support. We specialize in Odoo ERP software, an open-source platform that combines all these modules into one interface. Odoo’s modular, scalable solution grows with your business and cuts licensing fees (being open-source reduces cost).
Whether you’re in retail, manufacturing, services, real estate, or other sectors, Encloud can customize ERP to your needs. For example, our Odoo business solutions blog shows how integrated ERP tools improve time management and productivity. We also offer full ERP integration services to link your ERP with e-commerce, CRM, or legacy systems seamlessly.
In short, choosing an ERP doesn’t have to be confusing. With the right guidance, small business ERP can be affordable and transformational. We recommend starting with a free ERP trial or demo, mapping your core processes, and working with a consultant to ensure a good fit. Encloud Solutions can help you unlock the full power of ERP, streamlining operations and accelerating growth.
FAQs
What is the best ERP for small businesses?
There’s no one-size-fits-all answer, but several ERP packages stand out for small companies. Popular choices include Odoo (highly flexible, open-source), Microsoft Dynamics 365 Business Central, SAP Business One, Oracle NetSuite, and Sage Intacct.
Is ERP suitable for small businesses?
Yes, modern ERP systems are designed with small and mid-size businesses in mind. Cloud-based SMB ERP software often requires little IT overhead and charges affordable monthly fees. Even very small companies can benefit once they need more than basic spreadsheets. Statistics show many small firms already use ERP to unify operations. If your business struggles with disconnected systems or data entry work, an ERP can greatly improve efficiency and visibility.
What is ERP in small business?
ERP stands for Enterprise Resource Planning. In the context of small business, it means a single integrated software platform that manages core functions (finance, inventory, sales, purchasing, HR, etc.) together.
What size company needs an ERP?
Any company that is outgrowing basic accounting and spreadsheets may need ERP. There is no hard cutoff, but generally once you have multiple people handling inventory, orders, and finances, it’s time to consider it. Many SMB consultants suggest looking at an ERP once you reach 10+ employees or when you have multiple locations/departments to coordinate. If your business plans to grow (more users, more transactions), investing in SMB ERP software early can save headaches later.
Is there any free ERP software?
Yes, several ERP systems offer free versions. Notably, Odoo’s Community Edition is completely free and open-source, including 17 core modules (accounting, inventory, CRM, etc.). Another example is ERPNext, an open-source ERP that you can download at no cost. These free options let you use ERP functionality without licensing fees (you only pay for hosting or support if needed).
How to find companies looking for ERP?
Finding businesses in need of ERP usually means targeting growing companies or industries known for ERP use. There isn’t a public list of ERP-seeking companies, but you can look for clues: businesses advertising ERP project managers or consultants, companies mentioning digital transformation in news, or those posting challenges with operations. Common tactics include networking (industry events, LinkedIn outreach), content marketing (writing helpful ERP guidance so prospects find you), and strategic partnerships.
ERP Integration Services: A 2025 Guide on What, Why, & How
Understanding what ERP integration is is the first step for any business looking to connect its systems. In simple terms, enterprise resource planning integration is the process of linking an ERP system with other software (CRM, e-commerce, POS, etc.) so that data flows automatically between them. An ERP system is the hub of core processes (finance, inventory, sales, HR), but without integration, these functions can become siloed.
Effective ERP integration solutions ensure that information entered in one module (say sales orders) appears instantly in others (like accounting or inventory). For example, Oracle’s ERP Integration Service “provides external operations for ERP integration scenarios such as bulk data import and export to execute end-to-end inbound and outbound data flows”.
In practice, integration means your ERP can integrate with third-party tools via APIs or middleware, so you can focus on growing your business instead of re-entering data. ERP integration (sometimes misspelled ERP intergration) is fundamental for modern companies. By definition, ERP integration allows different departments to share real-time data to improve visibility and collaboration.
In other words, integrated ERP systems automate workflows between sales, inventory, production, etc., so your business runs smoothly. Many industry experts describe it as the “process of connecting disparate systems, such as ERP software, CRM systems, and other business applications, to ensure data flows efficiently and accurately”. As one Solix blog puts it, ERP integration services aim to make your systems “talk to each other seamlessly” so you spend less time on manual corrections.
Also Read: Best Zoho CRM Development Company
What is ERP Integration?
ERP integration definition involves syncing ERP data across your entire software stack. According to Flexspring, ERP integration refers to the process of connecting an ERP system with other business applications and data sources to create a seamless flow of information across the organization. For example, when you add a new customer in your CRM, ERP integration ensures that the record appears automatically in your accounting module. This unified approach, sometimes called integrated ERP, eliminates redundant work and gives everyone the latest data in one place.
1) Integration with ERP
Modern ERP platforms expose ERP APIs (application programming interfaces) so other apps can read/write data. An ERP system API is basically the bridge that other software uses to talk to your ERP. By using erp api integration, developers can connect point-of-sale apps, webstores, and even mobile tools directly to the ERP database.
For example, Odoo offers a rich XML/JSON API, and Oracle provides SOAP/REST endpoints. Pre-built ERP connectors or ERP connectors (for Shopify, Amazon, QuickBooks, etc.) often come as part of integration platforms, enabling fast setup without coding.
2) ERP Integration Software
There are dedicated ERP integration system products (often iPaaS tools) that handle the heavy lifting. These ERP integration software solutions (like Dell Boomi, MuleSoft, or Oracle Integration Cloud) act as middleware to map and transform data between systems. In these platforms, integration vendors provide connectors and templates for common use cases (e.g., e-commerce sync).
OrderEase explains that middleware “serves as the connective tissue between your ERP and other systems, enabling seamless communication and data exchange”. Whether via simple REST APIs or full ETL workflows, this software reduces manual coding.
Why ERP Integration Matters
ERP integration delivers huge benefits of erp integration for businesses of all sizes, especially SMBs. By linking your ERP with other tools, you can:
1) Eliminate Data Silos
Integration unifies data across functions. Instead of separate spreadsheets for orders, accounting, and inventory, integrated processes keep everyone on the same page. This means faster decision-making and fewer errors. As one industry guide notes, an ERP “unifies critical business functions, breaks down data silos, and gives employees a single source of truth”. For example, real estate firms using an ERP integration solution saw manual efforts reduced and efficiency increased by unifying financials and project data.
2) Boost Productivity
Automated data flows free your team from tedious tasks. For instance, OrderEase reports that linking ERP with sales channels “boosts productivity by eliminating manual tasks” such as re-entering orders. Your staff spend more time on strategic work and less on copying numbers. Solix also highlights productivity gains: their clients enjoy “massive cost savings and increased productivity” after ERP integration.
3) Real-Time Visibility
With integration, data updates instantly across systems. Sales reps, inventory managers, and accountants all see the current status without delay. As noted, APIs deliver “real-time updates instantly,” whether checking stock levels or financials. In practice, this means if a sale is made, your ERP system and warehouse both reflect it immediately, preventing out-of-stocks and billing errors.
4) Improved Data Accuracy
Automated syncing means fewer typos and reconciliation headaches. The DreamFactory blog explains that API-driven ERP integration ensures “all your systems are always in sync, providing reliable, consistent data”. Gone are the days of chasing down mismatched entries between CRM and ERP. According to OrderEase, consistent data across e-commerce and ERP “eliminates the need for manual updates” and maintains one “centralized, accurate source of truth”.
5) Operational Agility
Connected processes let you scale faster. Want to add a new sales channel or partner? Integrated systems can adapt without manual retooling. Encloud’s own Odoo ERP integration services include connectors for Shopify, WooCommerce, Amazon, and legacy systems, showing how new sales streams can plug in quickly. Similarly, a CRM and ERP integration means your sales team isn’t slowed by back-office delays. Overall, a unified ERP ecosystem “streamlines operations and simplifies workflows”.
6) Odoo’s Integrated Platform
Odoo’s integrated platform provides a single source of truth across business functions. For example, Odoo is an “all-in-one business software platform” that combines project management, CRM, sales, accounting, and more, helping organizations “streamline operations and improve visibility across every workflow”. This exemplifies integrated business processes with ERP systems; once data is entered (like a project task), it is immediately visible to sales, inventory, and finance. The result is a truly unified system where ERP connectivity means you spend less time on grunt work and more on growing your business.
Also Read: Odoo Business Solutions
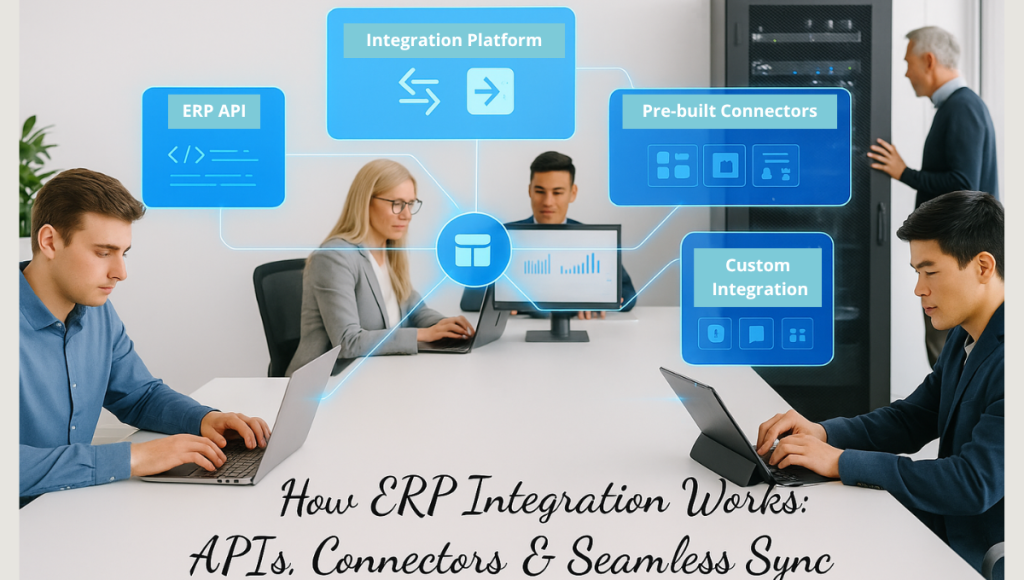
How ERP Integration Works (Methods & Tools)
ERP integration can be implemented in several ways, often using a combination of APIs, connectors, and middleware. The goal is always to get a reliable data flow between your ERP and other systems. Key components include:
1) ERP APIs
Nearly all modern ERP systems provide APIs. These are interfaces (REST, SOAP, etc.) that expose ERP data and functions to outside systems. For example, Oracle’s Integration Suite provides a SOAP API for ERP data flows, and Odoo has a flexible JSON-RPC/XML-RPC API for its objects. Using an erp api, developers can create integrations that push orders, invoices, inventory levels, etc., in real time. When done right, erp api integration makes different apps communicate like clockwork.
2) Integration Platforms (Middleware)
Integration middleware or iPaaS tools act as a bridge. These platforms handle data translation, routing, and scheduling so that each system doesn’t have to “talk to” every other system directly. In practice, a middleware solution manages data flows and keeps data consistent. As one integration guide explains, middleware solutions manage your data flow to maintain a centralized, accurate source of truth. Examples include cloud platforms like MuleSoft, Dell Boomi, SnapLogic, or industry-specific tools (OIC). These tools often have visual workflows and pre-built connectors.
3) Pre-built Connectors
Many ERPs and integration platforms offer connectors (also called ERP connectors or connectors). These are pre-packaged interfaces to common applications, e.g., connectors for Shopify, Amazon, QuickBooks, Salesforce, etc. Using connectors speeds up integration: you don’t start from scratch to link your ERP to a popular service. For instance, Odoo Integration Services include API connectors for Shopify, WooCommerce, Amazon, POS terminals, and even legacy ERPs. Likewise, Oracle’s OIC has an “ERP Cloud Adapter” specifically to link to Oracle ERP Cloud. Connectors usually handle data mapping and error-checking for you.
4) Custom Integrations
Sometimes off-the-shelf options aren’t enough, especially for unique business needs. In that case, companies may use custom ERP integration solutions. This involves writing tailored code or using specialized tools (and often hiring an ERP integrator or integration specialist). For example, a distribution company might develop custom APIs to sync its niche inventory system with SAP. Encloud Solutions emphasizes “tailored ERP solutions” and builds custom modules that fit unique processes. Custom integration ensures that even non-standard systems can plug into your ERP without compromise.
| Integration Approach | What It Does | Example |
| ERP APIs | Standard interfaces for programmatic access to ERP data and functions. Allows other apps to push/pull ERP data in real time. | Using Odoo’s JSON API to update inventory from a web store. |
| Middleware/iPaaS | Cloud or on-prem tools that orchestrate data flows, handle transformations, and centralize logic. Ensures data consistency across systems. | Oracle Integration Cloud or MuleSoft linking ERP with CRM. |
| Connectors & Integration Vendors | Pre-built adapters linking ERP to specific platforms (e.g., e-commerce, CRM). Offered by ERP vendors or third-party integration vendors. Speed deployment by using tested workflows. | Pre-built Shopify-Odoo connector, QuickBooks-SAP adapter. |
| Custom Integration | Bespoke development to connect specialized or legacy systems not covered by existing tools. Often done by an ERP integrator or an in-house team. | Building an API bridge between a custom CRM and Odoo ERP. |
Each method has a place. For best results, companies often combine them: use connectors for common apps and custom solutions for the rest.
ERP Integration Services & Specialists
Many businesses, especially SMBs, find it wise to hire experts for ERP integration. ERP integration services are offered by consultants and technology firms. An ERP integrator or an ERP integrator’s team can manage everything from planning to testing. These services usually include analyzing your current processes, defining integration requirements, selecting the right tools, and executing the data migration.
For example, the CommerceShop team highlights that professional services help you seamlessly connect your ERP system with other applications, tools, and software to automate your operations.
When evaluating providers, look for experience with your industry and platforms. Companies like Encloud Solutions specialize in Odoo ERP integration, meaning they know how to connect Odoo with e-commerce, CRM, or accounting software. On Encloud’s Odoo ERP service page, they list “Third-Party Integrations” for Shopify, HubSpot, Salesforce, etc., emphasizing API-driven integration to eliminate data silos.
Integration specialists will also set up security, error handling, and monitoring. They may be called ERP integration specialists or part of an integration vendor. In any case, professional services turn what could be a complex project into a smooth implementation.

Odoo ERP Integration: A Practical Example
For small businesses and SMBs, Odoo has become a popular ERP due to its modularity and affordability. Odoo’s suite already offers many built-in integrations (e.g., between Sales and Inventory), but you can extend it further. An Odoo ERP integration might link Odoo to your online store, point-of-sale, or legacy system. For instance, Encloud Solutions’ guide to Odoo ERP notes that their Odoo Integration Services include real-time connectors to Shopify, WooCommerce, Amazon, and even older ERP systems. This means if you’re using Odoo, experts can connect your sales, marketing, HR, and more, so your data is unified.
Odoo’s philosophy is “all your business on one platform”, and integration (Odoo) projects exemplify this. Its one-click apps approach means every module is natively integrated. As one blog on solar businesses explains, “Odoo is a full business suite where CRM is just one module. It integrates sales, inventory, projects, accounting, and more in one platform”.
In practice, Odoo CRM talks directly to Odoo Inventory; when a solar sales rep closes a deal, the Installation project and stock of solar panels in inventory are updated automatically. This eliminates the “data gaps” that generic CRMs often have. By leveraging Odoo’s open API and Encloud’s expertise, an integration Odoo project can connect even external apps seamlessly.
Many Encloud case studies and blogs highlight integration. For example, their Odoo Business Solutions: Time Management article shows how creative teams can use Odoo’s integrated ERP tools (timesheets, projects, CRM) to streamline work. Another blog, Best CRM for Solar Businesses, illustrates how Odoo’s unified approach boosts solar company workflows. In each case, integration means that once a data point (like a sales order or customer record) is entered, it’s immediately available across the system. This is the power of integrated business processes with ERP systems, and Odoo is built for it.

Benefits of ERP Integration for Your Business
The benefits of ERP integration cannot be overstated. By creating a connected ERP ecosystem, businesses enjoy:
1) Single Source of Truth
As Oracle notes, unified systems eliminate data duplication and provide a central repository. This means everyone, from sales to finance, is working off the same dataset.
2) Cost Savings
Reducing manual entry and syncing systems lowers error costs and admin overhead. Oracle points out that automating processes cuts down staffing and compliance costs. In one example, a cloud ERP saved a company half a million dollars by consolidating systems.
3) Faster Decisions
With data in real-time, managers can make quicker, better-informed choices. OrderEase explains that an integrated ERP gives real-time visibility across channels, speeding up growth opportunities.
4) Enhanced Collaboration
With all functions connected, teams collaborate more easily. Oracle says ERP “provides a single source of data and a common interface” so departments can share information without waiting on another team.
5) Scalability
Integration means your systems grow with you. Odoo’s modular approach (and its integration connectors) lets you add new capabilities or users without overhauling your ERP. Many SMBs start with core apps and expand, confident that the integrated framework will adapt.
Overall, ERP integration turns your ERP from a static database into a dynamic, orchestrated business hub. As one guide concludes, “Integrating your ERP can transform the way your organization operates, providing a centralized, seamless flow of information”.
Also Read: ERP for Small Companies
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What is ERP integration service?
are professional solutions that connect your ERP system with other business applications. An ERP integration service might include mapping data flows, configuring APIs/connectors, and implementing middleware. In technical terms, it’s the process of setting up “external operations for ERP integration scenarios” like bulk data import/export to streamline inbound/outbound flows. In short, ERP integration services help automate data exchange (orders, invoices, inventory) so your systems work together.
What is an ERP service?
An “ERP service” can refer broadly to any ERP-related offering, from software features to consulting. At a software level, it means modules and APIs within the ERP that perform business functions (e.g., Oracle’s financial suite includes ERP services for accounting). It can also mean implementation services. According to Oracle, ERP itself is “software that manages, automates, and connects day-to-day back-office processes” like accounting, procurement, HR, and more. So an ERP service might be, for example, installing or customizing these core modules for your company.
What is ERP in OIC?
In Oracle Integration Cloud (OIC), ERP typically refers to an enterprise resource planning system like Oracle Cloud ERP. OIC provides specialized adapters to connect with ERP applications. For instance, OIC has an “ERP Cloud Adapter” that lets you fetch or send data to Oracle ERP Cloud. Essentially, OIC acts as the integration layer – ERP is the core system being integrated. So “ERP in OIC” means using OIC to connect your ERP data (orders, financials, etc.) with other apps via OIC’s tools.
What is CRM and ERP integration?
This refers to syncing Customer Relationship Management (CRM) systems with ERP systems. CRM handles sales and customer data, while ERP handles back-office processes. Integration between them automates the handoff: e.g., a new customer in CRM automatically creates the account in ERP; a sales order in CRM generates an invoice in ERP. This ensures, as Solix puts it, that data “flows efficiently and accurately” between ERP and CRM systems. The result is one-click order processing, unified customer records, and fewer manual updates.
Is ERP better than CRM?
They serve different functions. ERP is not “better” or “worse” than CRM; they are complementary. A CRM focuses on front-office tasks (sales, marketing, service), and an ERP covers back-office (finance, inventory, HR). As Oracle explains, ERP systems support financial and operational functions, while CRM supports sales and customer service. Many modern businesses use both. Integrating them often yields better results than using one alone.
Is SAP an ERP or CRM?
SAP started as an ERP vendor. Its flagship products (like SAP S/4HANA) are ERP systems covering finance, manufacturing, supply chain, etc. SAP does offer CRM capabilities (formerly SAP CRM, now integrated into SAP C/4HANA), but traditionally, SAP is best known for ERP. In other words, SAP’s strength is back-office ERP functionality, with CRM modules available as part of its suite.
Odoo Business Solutions: How Does Creativity Work with Time Management in 2025
Everyone knows that time management is not easy for managing a successful business, especially if you wanna do something creative. Effective time management is the practice of planning and prioritizing your tasks so you can use your time more effectively to achieve business goals. Odoo ERP is an all-in-one business software platform that combines modules for project management, CRM, sales, accounting, and more. It helps organizations streamline operations and improve visibility across every workflow. In creative businesses, balancing open-ended innovation with strict schedules is crucial.
Want to see how Odoo ERP can improve your team’s time management? Fill out the contact form and get a personalized consultation.
After all, time is an irreplaceable asset, which is more valuable than money, because once it’s gone, you can’t get it back. Good time management lets teams focus on high-impact work: focusing on what matters most makes each work hour count. Lack of time control can suppress your creativity by forcing teams into reactive “fire‑fighting” mode instead of exploration. Odoo’s integrated business software suite helps creative teams plan, track, and automate workflows so they stay organized without stifling innovation.
Also Read: ERP for Small Companies
Importance of Time
Time is finite and must be managed carefully. Effective time management means you are meeting deadlines, increasing productivity, elevating work quality, and reducing stress, which establishes a culture of efficiency. We cannot extend time, so planning and prioritizing tasks is key.
Here is an example: scheduling focused creative blocks and clear deliverables ensures that each idea has a chance to develop. As one expert puts it, solid time management lets you clarify your goals, eliminate distractions, and focus your attention on your most essential activities. In other words, when teams respect the importance of time, they accomplish more with less effort and maintain better balance.
Consequences of Poor Time Management
When time isn’t managed well, creativity and productivity both suffer. The consequences of poor time management include missed deadlines, chaotic workflows, and stressed teams. Productivity suffers: people scramble to complete urgent tasks, quality drops, and professional relationships strain. Studies and expert guides report that chronic lateness or procrastination can strain relationships with colleagues, clients, and superiors, reduce job satisfaction, and stall careers.
Lack of time discipline can suppress creativity and innovative thinking because teams never have the slack to brainstorm or iterate. Financially, poor scheduling can waste resources and balloon project costs, as failing to control time leads to burnout and lost opportunities. By contrast, mastering time prevents these pitfalls: projects stay on budget, decisions improve, and people feel more in control.

Time Management Exercises
You can build time management skills through practice because regular exercises and habits help teams sync creativity with schedules within creative industries and commercial teams. For example, many companies hold brief daily stand-ups or weekly planning sessions to set goals and deadlines.
Teams adopt these time management exercises, from focused ideation sprints to structured review meetings, which create accountability without killing innovation. Practices like time-blocking (allocating set hours to design work) or keeping a “not-to-do” list (deciding which tasks to skip) train people to guard their creative time. Below are some key exercises that high-performing teams utilize to manage their time:
Target Setting
Define clear objectives or deliverables for each project phase. For creative projects, this mean setting a goal like “sketch 5 concepts this week” or “complete storyboard draft by Friday.” Clear targets guide teams’ energy and prevent scope creep.
Focus on What Matters Most
Prioritize tasks by impact. As Stephen Covey advised, “The key is not to prioritize what’s on your schedule, but to schedule your priorities”. In practice, this means identifying the 1–3 tasks that move a project forward and doing them first. Odoo’s tools can help: you can flag or filter the highest-priority tasks in a Kanban board so the team always “swim with the main current” of work.
Establish a Timeline
Assign deadlines and milestones to tasks. Breaking work into a timeline prevents last-minute rushes. Odoo’s Project app offers a Gantt view, “a timeline that gives you an overview of your tasks, their dependencies, and planned dates”. Creative teams can visualize progress and spot bottlenecks early by scheduling tasks on a timeline.
Contact us today to get a customized Odoo ERP demo tailored to your team’s workflow.
Write Down What to Skip
Consciously decide which tasks are low-value and can be dropped or deferred. Maintaining a “don’t do” list is as important as a to-do list. For instance, a designer might note that checking all email once per day is sufficient, so they don’t let constant pings steal creative time. This exercise helps teams focus on what matters most by not getting bogged down in trivialities.
Utilize Odoo Business Software
Leverage Odoo’s integrated ERP features for time tracking and analysis. Odoo is a project app and full business suite. For example, you can log billable hours with the Timesheets app, link tasks to accounting, or use Odoo CRM to set sales or project targets. Encloud Solutions reports that Odoo is used by millions of businesses worldwide; its all-in-one nature means you spend less time switching apps and more time being productive.
Also Read: ERP Integration Services

The table below summarizes how these exercises map to Odoo features:
| Exercise | Purpose | Odoo Application |
| Target Setting | Define clear goals and outcomes to guide activities | Use Odoo Goals, CRM targets, or project milestones to track objectives and progress. |
| Focus on What Matters Most | Prioritize key tasks that contribute most to objectives | Mark tasks as high-priority in Odoo Projects; filter the Kanban board by importance. |
| Establish a Timeline | Allocate deadlines and milestones for tasks | Use Odoo Project’s Gantt chart – a timeline overview of tasks and dates. |
| Write Down What to Skip | Identify low-value tasks to avoid wasting time | Keep a “not-to-do” list outside Odoo; use task tags or statuses to denote blocked tasks. |
| Utilize Creative Project Management Tools | Use visual, flexible tools for planning creative work | Odoo Projects offers Kanban (sticky-note style) and Gantt (timeline) views. |
| Utilize Odoo Business Software | Leverage an integrated ERP to centralize operations | Apply Odoo Apps (Timesheets, CRM, Projects, etc.) for unified planning, tracking, and billing. |
How to Be More Time Efficient with Customized Odoo ERP
Odoo’s modular ERP can be customized to enforce time discipline and visibility across projects. For instance, keeping on track is easier when progress is transparent: Odoo’s Project dashboard shows live updates on tasks, resources, and profitability so everyone sees the project’s status in real time. Team leads get alerts on delays, and the system automatically logs changes.
To never miss a deadline, Odoo lets you set task deadlines and milestones that trigger reminders. For example, the Timesheets app logs work hours against tasks so managers can spot overruns early. You can even invoice by time logged, reinforcing the habit of accurate tracking.
For detailed time tracking analysis, integrated reporting is key. Encloud Solutions’ Versatile Time Logger System can tie into Odoo and other CRM tools for in-depth time reports. Odoo itself generates reports on time spent per project, helping identify bottlenecks. You can analyze which tasks consumed more time than planned, spot trends across teams, and refine future estimates. Interested in optimizing your workflows? Fill out our contact form and let our experts guide you through Odoo ERP customization.
In practice, many Odoo customers create custom dashboards (using Odoo Studio) to track the most relevant KPIs for their creative workflows – for example, “average hours per design iteration” or “ratio of planned vs. actual effort.” These insights close the loop: the next time a creative project starts, teams know where they overscheduled or under-delivered.
Also Read: Odoo ERP Software
Throughout this process, Odoo’s flexibility lets you tailor the system. Need a built-in Pomodoro timer? There are Odoo apps for that. Want automatic reminders for routine tasks? Use Odoo’s Scheduled Actions. By utilizing Odoo business software, you transform time management from guesswork into a data-driven discipline. This allows creative staff to focus on innovation, knowing that processes and tools are keeping the schedule in check. Ready to manage your time more efficiently with Odoo ERP? Contact us today or fill out the form to get started.

FAQs
How do creatives manage their time?
Creative professionals often set creative rituals and use disciplined planning. For example, they dedicate fixed time blocks to ideation and to routine tasks. According to productivity guides, creatives “establish creative rituals, prioritize tasks, and use time blocking techniques.” By assigning specific time slots for innovation, they boost productivity while maintaining consistency.
What is the 7-8-9 rule for time management?
The 7-8-9 rule is a simple guideline: spend 7 hours on sleep, 8 hours on work or study, and 9 hours on everything else (meals, exercise, personal time). In theory, this balances rest, focused work, and life’s other needs, helping ensure you’re rested and productive.
How does time affect creativity?
Time affects creativity in two ways. Having too little unstructured time can suppress creative thinking, because people rush between tasks. On the other hand, well-designed routines or changes in routine can boost creativity. For example, varying your routine stimulates the brain and can “increase focus, productivity, and even creativity and innovative thinking”. In short, structured time blocks free the mind to create, but too rigid a schedule can be stifling.
What is the 60/40 rule for time management?
The 60/40 rule advises spending roughly 60% of your available time on your biggest, goal-advancing tasks and 40% on everything else. In other words, focus most of your week on the projects that move the needle, and leave the remaining time for routine duties (emails, admin, errands). High performers found that using a 60/40 split helps prevent burnout and ensures critical goals get done.
What are the 5 P’s of time management?
A popular framework is the “5 P’s” of time management. They are Prioritize (do the most important tasks first), Plan (schedule and allocate time for each task), Productivity tools (use apps or systems to streamline work), Proactive mindset (anticipate challenges instead of just reacting), and Personal well-being (schedule breaks and self-care to stay energized). Together these guide efficient, balanced workflows.
How does routine affect creativity?
Routine has a double-edged effect. A consistent routine provides structure and stability, which can help free cognitive resources. However, overly repetitive routines may lead to autopilot behavior and boredom. Changing up your routine even slightly can “stimulate your brain” and boost creativity. Creative teams often balance routine (for discipline) with variety – for example, they may hold random “innovation days” or change work environment to keep ideas fresh.
Which skill is most essential for time management?
One widely cited essential skill is prioritization. Being able to assess which tasks matter most and scheduling them first makes all other planning worthwhile. In practice, this means identifying the critical few tasks (the “big rocks”) and focusing on them before lesser items. Experts note that scheduling your highest priorities ensures you invest time where it has the greatest impact.
Odoo ERP Software in 2025: A Complete Guide for Your Business Optimization
Companies demand ERP platforms that balance cost, flexibility, and functionality within today’s digital economy. Odoo ERP software is utilized by 7M+ users in 120+ countries (an estimated 15% share of the global open‑source ERP market within the year 2024). IDC projects the mid‑market ERP segment to grow at 8% CAGR through 2027, with Odoo cited as a leading growth driver due to its modular architecture and affordability.
In this guide, you will learn about what Odoo ERP software is, critical Odoo ERP system features, market alternatives comparison, and how Encloud Solutions’ Odoo ERP implementation services ensure ROI.
→ Want to see how Odoo fits your business? Fill out the quick form below to get a free consultation from our ERP specialists.
What Is Odoo ERP Software?
Many professionals thought, “What is Odoo ERP System?” So, here is the answer. Odoo ERP software is an integrated suite of business applications that covers CRM, accounting, manufacturing, inventory, HR, and more.
The platform’s open‑core model offers:
- Community Edition: Free, LGPL‑licensed, includes 17 core apps. Widely adopted by startups and open‑source advocates.
- Enterprise Edition: Proprietary modules, white‑glove hosting, SLA-backed support, and Studio for drag‑and‑drop customizations.
Deployment Modes
- On‑premise: Full data control for regulated industries.
- SaaS: Fully managed cloud at $25/user/month with automatic updates.
- Odoo.sh: Platform‑as‑a‑Service (PaaS) combining the flexibility of source code with cloud convenience.
Global Compliance & Localization
This system is available in 60+ languages in compliance with GDPR, VAT, GST, and other regional tax regimes. Its partner network of 2,200+ certified firms spans 100 countries, which ensures local expertise and implementation quality.

Odoo ERP System Features
Odoo’s appeal stems from its extensive feature set, all united on a single platform. The following are the key Odoo ERP System features:
- Modular Architecture: 30+ official modules, 20,000 community apps for industry‑specific needs (Healthcare, Education, Agriculture).
- Real‑Time Reporting & BI: Native BI engine with drag‑and‑drop report building. Companies report 25% faster financial closes.
- AI & Automation: According to the Odoo case study, 2023, automated lead scoring increases sales productivity by 30%.
- Mobile Accessibility: Progressive Web App (PWA) supports offline mode for inventory and field service teams.
- User Permissions & Security: Role-based access control, two‑factor authentication, and SOC 2 compliance.
Top Odoo Features & Their Benefits
| Feature | Benefit |
|---|---|
| Modular Apps | Only pay for what you use and scale modules over time |
| Real‑Time BI & Dashboards | Identify trends instantly and accelerate decision cycles by 35% |
| Automated workflows & AI | Reduce manual tasks by 40%, which frees staff for higher‑value work |
| Progressive Web App | 24/7 field access, even without connectivity |
| Partner Network (2,200+ firms) | Localized support, faster implementation, adherence to best practices |
ERP Software Odoo vs. Competitors
ERP Software Odoo shines through its blend of affordability and extensibility within the competitive ERP landscape.
| Criteria | Odoo | SAP Business One | Microsoft Dynamics 365 |
| Licensing Cost | $0–25/user/month | $1000+/user one‑time | $70+/user/month |
| Implementation Time | 2–4 months (SMB) | 6–12 months | 6+ months |
| Customization Effort | Low (open source, Studio tool) | High (ABAP required) | Medium (Power Platform) |
| App Marketplace | 20,000+ modules | Limited third‑party apps | Moderate (AppSource) |
| User Satisfaction | 4.3/5 (G2) | 3.8/5 (Peer reviews) | 4.0/5 |
Independent analyses show Odoo’s five‑year TCO at 40–60% lower than SAP and Dynamics, which makes it the top choice for agile mid‑market firms.
Also Read: Odoo Business Solutions

Trends & Industry Benchmarks Adoption
If you understand market trends, it helps validate your ERP choice. You can consider the following key data points:
- Segment Growth: According to Forrester, the Cloud ERP market will exceed $60 B by 2026, with SMB solutions growing the fastest.
- Regional Uptake: APAC shows 12% annual growth in ERP deployments; MENA is up 15% as digitalization accelerates.
- Top Industries: Manufacturing (25% share), Retail (18%), Services (15%), Distribution (12%).
This data highlights the strategic advantage of early ERP adoption. Companies report a 20% boost in operational efficiency within 12 months of going live.
From ERP Demo Online to Full Odoo Implementation
Begin your journey with a hands-on ERP demo online. Encloud Solutions’ structured approach includes:
- Discovery Workshop: Align ERP capabilities with business objectives and map 10+ core processes.
- Proof of Concept (PoC): Live sandbox with sample data; measure key metrics (order cycle time, lead conversion).
- Implementation Blueprint: Document requirements, customization scope, and data migration plan.
- Go‑Live & Stabilization: Post‑launch hypercare; target SLA: <1% downtime, ticket resolution <4 hours.
Explore our Odoo ERP service page for step-by-step guidance.
Odoo Integration Services & Odoo Implementation Services
Connecting Odoo tightly to your ecosystem multiplies its value.
- Odoo Integration Services: It includes real-time API connectors for Shopify, WooCommerce, Amazon, POS terminals, and legacy ERPs.
- Odoo Implementation Services: Odoo implementation project management covers:
- Installation & configuration of 30+ modules
- Custom module development (Python & JavaScript)
- Data migration (CSV, XML, API) with 99.9% accuracy
- UAT, training workshops, and change management plans
Case in point: a global distributor integrated Odoo with five logistics partners, which cut shipping delays by 25% within three months.
Sustained Success: Odoo ERP Support & Odoo Consulting Services
A support framework ensures your ERP remains an asset, not a liability.
- Odoo ERP Support: Odoo ERP support system includes 24/7 helpdesk, monthly patch updates, performance monitoring, and security audits in alignment with ISO 27001.
- Odoo Consulting Services: Quarterly business reviews, process re-engineering, and roadmap planning for future modules.
Client success story: a service firm reduced process redundancies by 30% after a consulting-led workflow optimization.
Also Read: Best CRM for Solar Businesses
Choosing the Right Partner
Your ERP project’s success hinges on partner expertise; that’s why you should consider the following points before choosing the right Odoo implementers, installers & developers :
- Odoo ERP Software Development Company: They should have deep technical skills for bespoke apps, AI/ML features, and mobile solutions.
- Odoo Implementer & Odoo Implementation Partner: Their team should consist of certified functional and technical consultants who guide full-cycle rollouts, including Odoo ERP installation.
Encloud Solutions is a certified Odoo ERP services provider, with 100+ global deployments, 98% satisfaction, 4.8/5 average partner rating on Odoo’s directory.
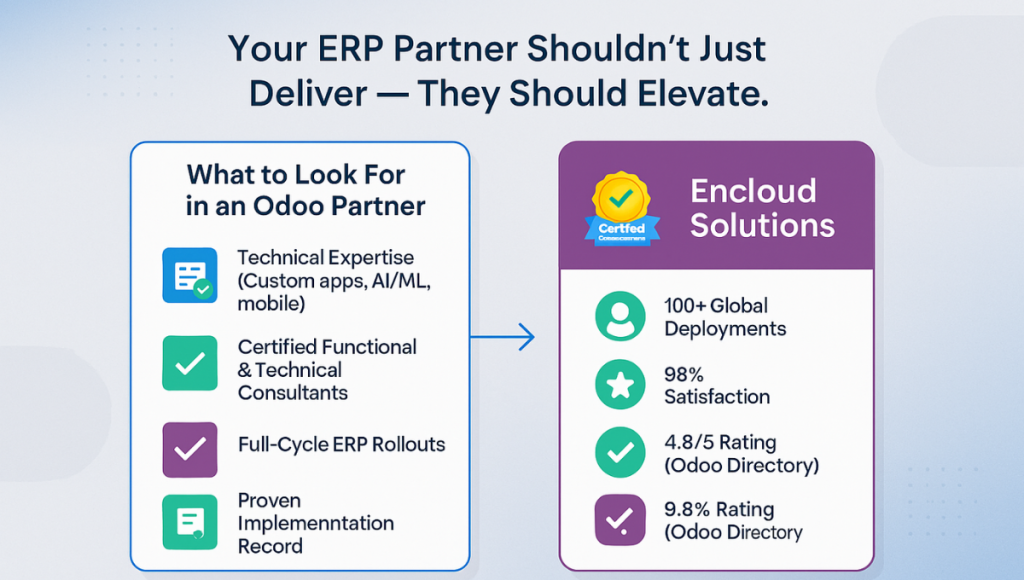
Use Cases: Odoo Business Solutions
Here we are discussing the use cases of Odoo ERP. Odoo’s flexibility serves diverse needs:
- Startups & Entrepreneurs: Launch with core CRM and invoicing; add Inventory and POS as revenue scales.
- Odoo for Small Business: Leverage Odoo for small business bundles—Sales, Accounting, and Inventory at <$100/month.
- Consultancies & Agencies: Use Project and Timesheets for client billing and resource planning.
- Multi‑National SMEs: Manage subsidiaries, multi‑currencies, and consolidated financial reports from a single database.
These Odoo business solutions deliver ROI within 6–12 months through process standardization and automation.
Planning Checklist for Your Odoo Implementation
Here is the planning checklist for your Odoo Implementation, which will help you during the system execution:
- Define clear KPIs (cycle times, revenue growth).
- Select Community vs Enterprise with cost analysis.
- Audit and cleanse legacy data.
- Schedule ERP demo online and PoC.
- Engage a certified Odoo implementation partner.
- Develop training and change management plans.
- Monitor post‑go‑live SLAs and continuous improvement.
This checklist ensures structured execution and measurable outcomes.
Also Read: ERP Integration Services
FAQs
Is Odo’o an ERP software?
Yes, Odoo ERP software is a comprehensive suite covering CRM, sales, accounting, inventory, manufacturing, HR, and more. Its modular design lets you start small and expand functionality as needs change, which supports businesses from 1 to 1,000+ users.
Which is better, SAP or Odoo?
SAP targets large, complex enterprises with extensive budgets. On the other hand, ERP software Odoo prioritizes agility, lower TCO, and rapid ROI, which is ideal for SMBs and mid‑market firms. Independent studies show Odoo’s five-year TCO is up to 60% less than SAP Business One.
Is Odoo available in Pakistan?
Yes, both cloud and on‑premise editions serve Pakistani businesses. Local partners handle localization for GST, income tax, and compliance with the State Bank of Pakistan’s guidelines on financial reporting.
Is Odoo software free?
The Community edition is open-source with no license fees. The Enterprise edition requires subscription fees for premium modules, hosting, and official support, which start at $7/user/month for essential apps.
How much is Odoo per month?
Enterprise pricing ranges from $7 to $25 per user/month based on the modules selected. Annual commitments may yield up to 20% discounts.
Is Odoo good for beginners?
Yes, Odoo ERP software features intuitive UIs, interactive setup wizards, and extensive documentation, plus community forums. Beginner-friendly training courses and certifications are available directly from Odoo and partners.
Can we earn money from Odoo?
Yes, you can earn money by working as an Odoo implementer, developer, functional consultant, trainer, and support engineer. Certified professionals earn competitive rates ranging from $30 to $150/hour globally.
Best CRM for Solar Businesses: Why Odoo is a Top Choice
Solar companies from solo installers to large enterprises deal with complex sales cycles, lengthy proposals, and on-site project coordination. Managing all this with spreadsheets and disjointed tools leads to inefficiency. Analysts note that installers often struggle with “complex proposal creation, bad project management, [and] poor lead management,” which slows growth. A dedicated solar CRM centralizes customer data, automates workflows, and ensures no lead falls through the cracks.
Key Features of a Solar CRM
The right CRM for solar business offers these essentials:
- Lead and Pipeline Management: Capture and prioritize leads from websites, referrals or campaigns. Track prospects through every stage of the sales funnel. With a solar pipeline CRM, companies can better visualize and close deals faster.
- Automated Proposals and Quotes: Generate accurate solar CRM software quotes and financing proposals quickly. Integrations with design or pricing tools ensure system specs and ROI calculations populate automatically.
- Project Scheduling and Field Service: Once a deal is won, automatically create an installation project. Use shared calendars or Gantt views to schedule site surveys and tasks. Field crews can update jobs on mobile, recording time, parts used, and progress on site.
- Customer Follow-up and Support: Automate follow-up emails, warranty reminders, and service tickets after installation. Keeping customers informed builds trust and boosts referrals with a strong solar company CRM in place.
- Reporting and Analytics: Dashboards show KPIs like lead conversion rates and average deal size. Custom reports reveal bottlenecks in the sales process and opportunities for improvement.
Integrating these features yields big benefits. As Nutshell observes, a solar industry CRM provides “streamlined lead management,” automated tasks, data-driven insights, and enhanced collaboration. In practice, this means less manual work and more consistent sales.
Also Read: Odoo Business Solutions
Solar CRM Options: Specialized vs. Integrated
Several CRM products target the solar industry. Niche tools like SPOTIO or Shape CRM have templates for solar canvassing and lead routing. For example, SPOTIO touts itself as “the #1 best CRM for solar sales and Sales Software” for field sales teams. These specialize in mapping, territory management, and multi-channel outreach.
General-purpose CRMs like Salesforce or HubSpot can be customized for solar, but often require extra setup for industry-specific workflows. In contrast, Odoo is a full business suite where CRM is just one module. It integrates sales, inventory, projects, accounting, and more in one platform. It is literally designed as “a suite of open source business apps that cover all your company needs: CRM, eCommerce, accounting, inventory, point of sale, project management, etc.”. This unified approach helps solar companies manage all operations without data gaps with an all in one solar CRM.
Why Odoo Stands Out
Odoo combines CRM with project management and back-office tools. According to experts, it “reduces every aspect of a business into a single, integrated platform” and offers solar firms tools to simplify operations and cut costs. On Odoo’s solar industry page, it highlights a “centralized pipeline” for leads and “all-in-one project management” with automated project creation after a sale. In practice, this means when you close a deal, Odoo automatically generates the installation project and task list.
Beyond sales, Odoo covers the entire solar lifecycle. It includes an Inventory module for tracking panels, inverters, and batteries in real time. You can set reordering rules to prevent stockouts and manage multiple warehouses. The Accounting app ties everything together: invoices are linked to sales orders and projects, and financial dashboards keep tabs on cash flow. For example, spare parts used in the field can be invoiced on the spot via the mobile app, and the system immediately updates the financials.
Odoo is also modular and scalable. You can start with core apps (CRM, Projects) and add advanced features (Field Service, IoT integration, etc.) as needed. This keeps initial costs lower. In fact, by centralizing workflows, Odoo “eliminates the need for multiple software systems,” reducing licensing and support costs. As your solar firm grows, Odoo grows with it: its modular structure lets you add new branches, users, or applications without ripping out the system. For companies evaluating options, learning how to choose solar CRM is critical, and Odoo often emerges as the best CRM for solar company due to its scalability.
Also Read: What Is Property Management Software
Odoo’s Solar-Focused Capabilities
Odoo’s suite hits all the right notes for solar businesses:
- CRM & Lead Tracking: Every lead is logged and scored in Odoo. Representatives follow up on calls or emails directly through the system. Detailed records mean sales teams never lose track of a prospect, even if someone leaves the company. This makes Odoo a reliable custom solar CRM solution.
- Project Management: Treat each installation as a project. Managers create tasks (survey, permits, install) with deadlines and assign them to team members. Gantt and Kanban views keep schedules transparent so projects finish on time.
- Field Service App: Technicians receive jobs on mobile. They update job status, log hours, and note spare parts used. Managers see real-time progress. This mobile capability greatly boosts field productivity and positions Odoo among the best solar sales CRM platforms.
- Inventory & Supply Chain: Odoo tracks hardware and parts by serial or batch. Barcode scanning and automated reorders prevent missing components. By consolidating inventory with sales, companies avoid expensive overstocking or shortages.
- Invoicing & Reporting: Generate invoices directly from projects or sales orders. Odoo auto-populates customer info and terms, speeding up billing. Its reporting tools turn project data into dashboards, so businesses can analyze performance and forecast growth in real time.
Together, these capabilities “break down silos” between departments. Sales, installation crews, and finance all work from the same data. For example, if a customer calls about their system, the team can instantly see contract details, past service appointments, and billing history in Odoo – a 360° customer view that generic tools seldom provide.
Choosing the Best Solar CRM

Not every company will pick the same tool. A solo installer might start with a lightweight solo solar CRM, while an enterprise may need a heavy-duty ERP. Key considerations include mobile support for field staff, integration with solar design or accounting software, and total cost of ownership. Make sure the CRM handles maintenance schedules and follow-ups as well. Also look for multi-currency and multi-language support if you operate in the US or Europe. It helps to have an implementation partner too. For instance, enCloudSolutions has deep experience customizing Odoo for solar workflows, ensuring the solution fits your needs. Odoo’s popularity means there is ample expertise available; certified partners can customize the system and train your staff, smoothing the transition. Odoo is designed to scale: a small installer can start with a few users and add modules as they grow to serve larger markets. This flexibility makes Odoo one of the best solar CRM software choices available.
Also Read: Odoo ERP Software
Conclusion
In the booming solar industry, effective CRM is no longer optional. Companies that adopt a CRM solar solution can manage leads, proposals, installations, and after-sales service all in one place. While specialized tools like SPOTIO excel at field canvassing, Odoo offers an all in one solar CRM business management platform. By combining CRM, project tracking, inventory and finance into one package, Odoo helps solar teams “operate projects, optimize inventory, [and] serve clients effectively”.
In practice, using Odoo can turn chaotic spreadsheets into smooth workflows. As one user put it, the platform made it “easier for our people to do things in a standard way and in a smarter way”. For U.S. and European solar businesses ready to scale, Odoo is a top contender especially with knowledgeable partners to guide implementation. By choosing the right CRM (like Odoo), you can focus on growing your solar business instead of juggling siloed systems.
Sources: We reviewed industry analyses and vendor materials (Sunbase Data, Nutshell, Spotio, Odoo, Ksolves) to compile these insights on solar CRM needs and Odoo’s advantages.
FAQs
Can I use Solo with my current CRM like Salesforce, Solar Cloud, or Solar CRM?
Yes, Solo can work alongside popular CRMs like Salesforce, Solar Cloud, or Solar CRM. Many solar businesses use Solo to handle proposals and design while keeping their CRM for customer tracking. This integration makes your workflow smoother because you can keep client data in your CRM and let Solo handle the project-specific tasks.
What support channels are standard for solar business platforms?
Most solar business platforms provide multiple support options such as email, live chat, phone support, and knowledge bases with tutorials. Some even offer dedicated account managers or training sessions. Having these channels helps solar companies quickly resolve issues, get product updates, and train their teams without losing time on projects or customer interactions.
Does Solo offer analytics or reporting tools for solar businesses?
Yes, Solo offers reporting and analytics tools that help solar companies track performance, sales, and project progress. These insights allow teams to see how proposals are converting, where bottlenecks are happening, and how to improve operations. Having data in one place makes it easier for solar contractors to make informed decisions and grow.
How do I switch my back-office operations from Sunbase to Solo?
Switching from Sunbase to Solo involves migrating your customer data, project details, and workflows. Usually, Solo’s support team helps guide this process with onboarding assistance. You’ll export data from Sunbase, set up your team on Solo, and adjust settings to match your processes. With training and support, the transition can be smooth and quick.
How do leading back-office platforms for solar integrate with other business apps?
Top back-office platforms for solar integrate with tools like CRMs, payment processors, project management apps, and accounting systems. This integration makes sure customer info, sales data, and financial records stay connected. Instead of switching between different systems, solar teams can access everything in one place, saving time and reducing the chances of mistakes.
What are the most effective back-office solutions for solar contractors?
The best back-office solutions for solar contractors are platforms that combine proposal design, project management, customer tracking, and reporting. Tools like Solo, Sunbase, or JobNimbus are popular because they simplify day-to-day operations. An effective solution helps contractors spend less time on paperwork and more time delivering projects, which means faster growth and happier customers.
What benefits do solar companies get from a single platform for sales and operations?
Using a single platform brings all data and workflows together. Solar companies can create proposals, track leads, manage projects, and process payments in one place. This reduces errors, saves time, and keeps teams on the same page. With everything connected, sales and operations work faster, which helps companies close more deals and complete projects smoothly.
How do solar CRM platforms help manage leads and projects for installers?
Solar CRM platforms help installers capture leads, track their progress, and convert them into projects. Once a lead turns into a project, the CRM manages schedules, tasks, and customer communication. This keeps everything organized from first contact to installation. By reducing manual tracking, CRMs make sure installers don’t lose leads or miss important steps.
What should enterprises look for in an energy CRM platform?
Enterprises should look for an energy CRM that supports lead management, project tracking, integrations with other apps, reporting, and customer communication. The platform should also be easy to use, mobile-friendly, and scalable as the business grows. A good energy CRM doesn’t just store data, it streamlines workflows and helps teams close deals faster while staying organized.
What Is Property Management Software?
Property management software is specialized technology that streamlines the daily operations of landlords and property managers. It replaces manual tools (spreadsheets, paper records) with a centralized system for tracking leases, rent payments, maintenance, accounting, and tenant communications. In practice, a property management system (PMS) lets users organize tenant/lease data, collect online rent, process maintenance requests, and generate financial reports all in one place. Modern PMS platforms are usually cloud-based, offering anytime access via web or mobile apps and real-time collaboration across teams. In short, PMS automates routine tasks and data entry, helping managers focus on strategy rather than paperwork.
Who Uses Property Management Software and Why

Property management software is widely used by residential and commercial real estate professionals – including individual landlords, property managers, REITs and investment firms. Users range from small landlords handling a few units to large firms with hundreds of properties.
Those who adopt PMS do so to scale operations and reduce errors: a dedicated system can handle growing portfolios by unifying processes (tenant screening, lease renewals, owner payouts, etc.) in one place. Key stakeholders – from owners/landlords to third-party managing agents – rely on PMS to stay compliant and provide better service. For example, in the UK integrating PMS with Making Tax Digital (MTD) rules became crucial after 2019, as systems now automatically maintain digital VAT records and generate returns. In essence, property owners use PMS to save time, cut administrative overhead, and improve tenant satisfaction through faster communication and automated workflows.
- Streamlined Operations: Rather than juggling spreadsheets or separate apps for accounting and leasing, a PMS centralizes all property data and workflows.
- Scalability: Dedicated software can easily expand as portfolios grow. Managers can add units or new properties without hitting the limits of manual systems.
- Automation: Routine tasks like rent collection reminders, work order assignments, and late fee calculations become automated, reducing manual effort.
- Improved Accuracy: Built‑in accounting and reporting tools minimize errors in financials and audits, offering tenants and owners transparent statements.
Overall, the ROI comes from saving time and money. Industry experts note that PMS “helps simplify and automate various tasks such as tenant management, rent collection, maintenance tracking, and financial reporting”, which enhances efficiency and frees managers to focus on business growth.
Also Read: Odoo ERP Software
Key Features of Modern PMS
Contemporary property management systems bundle numerous features tailored to real estate workflows. While exact capabilities vary by vendor, most include:
- Lease & Tenant Management: Centralized tracking of lease terms, expirations, renewals and tenant history. Many systems include online lease signing and applicant screening tools. This streamlines tenant onboarding and vacancy filling.
- Online Payments & Accounting: Automated rent collection via integrated payment gateways, plus trust accounting or general ledger modules. PMS software often generates owner statements and handles security deposit accounting, reducing bookkeeping errors.
- Maintenance & Work Orders: Portals or mobile apps to submit maintenance requests and assign vendors. A good PMS logs work orders and tracks maintenance costs, improving service response and compliance.
- Communication Tools: Built-in messaging (email/SMS) linked to tenant profiles and reminders for tasks like lease renewals. This keeps all communications in one place and automates notifications.
- Online Portals: Secure tenant and owner portals where users can view statements, make payments, and submit requests. Such self-service portals boost transparency and reduce calls/emails to managers.
- Document Storage: Digital repositories for leases, invoices, inspection reports and photos. Storing documents in the PMS ensures they are organized and accessible for audits or compliance.
- Reporting & Analytics: Customizable dashboards and reports on occupancy rates, rental income, expenses, maintenance trends, etc. Data analytics (often AI-powered) can forecast issues (like upcoming vacancies) and support pricing decisions.
- Budgeting & Forecasting: Tools to create budgets, track expenditures, and project future cash flows for a property or portfolio, aiding long-term planning.
- Integration & Customization: Many modern PMS platforms allow connections to CRM systems, IoT devices (smart locks, sensors) or accounting software like QuickBooks. Highly configurable systems let managers tailor workflows to complex scenarios.
In practice, one review notes that commercial PMS tools may add features such as Common Area Maintenance (CAM) reconciliation, multi-tenant expense tracking, and advanced lease abstraction (for percentage rents or escalations). Likewise, hospitality‐focused PMS might integrate room reservations and point-of-sale billing. When choosing software, managers should align features with their operational needs and property types.
Also Read: Best Real Estate ERP Software
Residential vs Commercial Software
Not all property management software is one-size-fits-all. Residential PMS is typically geared toward landlords of apartments, condos or single-family homes. It emphasizes features like online applications, one-rate rent schedules, and tenant screening. In contrast, commercial PMS is designed for office buildings, retail centers, industrial parks, etc., and handles more complex scenarios. Commercial properties often involve multiple tenants per unit, specialized lease types (e.g. triple-net, gross leases), and additional expense billing. A commercial system will usually include modules for recovering operating expenses, managing CAM charges, and tracking vendor contracts – elements usually absent from basic residential software.
For example, one guide explains: “commercial property management software… often incorporates complex lease structures, including options for triple net leases and gross leases. It usually includes tools to manage operating expenses, service requests, and vendor contracts”. In practice, this means a commercial solution will let you automate CAM reconciliations and expense allocations that residential tools do not.
On the other hand, using a commercial platform for a simple residential portfolio can be overkill. Therefore, it’s crucial to match the software type to your properties: small landlords may do fine with entry‐level residential PMS, while large owners of office or retail space need the advanced financial and compliance features of a dedicated commercial PMS.
Technology and Trends in Property Management

Property management software is part of the broader PropTech (property technology) boom. The market is evolving rapidly, driven by cloud computing, mobile access, and emerging technologies. Cloud-based SaaS solutions now dominate the industry, valued for their accessibility, automatic updates, and low upfront costs. Mobile apps let managers handle tasks on-the-go and offer tenants on-demand access to services.
Beyond basic functionality, advanced technologies are reshaping PMS today:
- Artificial Intelligence & Analytics: Modern systems use AI/ML to analyze occupancy and financial data. This enables predictive maintenance (identifying likely failures before they happen) and dynamic pricing suggestions for rent. For instance, a PMS might forecast budget overruns or optimize utility usage based on historical trends.
- Smart Building Integrations: IoT and smart devices are more common in managed properties. PMS platforms can connect to smart thermostats, security cameras and energy meters, allowing remote monitoring and proactive operations. For example, sensors might alert managers to water leaks early, or optimize HVAC settings for energy efficiency.
- Virtual Tours & Contactless Services: Especially after 2020, virtual leasing features (3D tours, online lease signings) have become trends. Some PMS suites offer integrated virtual showing and e-signature tools to facilitate tenant moves without in-person contact.
- Enhanced Tenant Experience: Systems now often focus on tenant self-service and engagement. This includes chatbots for common questions, tenant mobile apps for issues reporting, and flexible payment portals. The goal is to improve satisfaction by making operations transparent and user-friendly.
- Security & Compliance: With so much data, providers emphasize security (encryption, access controls) and regulatory compliance (GDPR in Europe, digital VAT records for UK, etc.). Top systems offer role-based access and audit trails to keep both tenant and owner data secure.
These trends underline that a PMS is no longer just an electronic ledger – it’s an integrated technology platform that leverages data. By adopting the latest tools, property teams can work more efficiently and focus on strategic goals. As one analysis notes, the global PMS market is growing quickly: it was estimated at $24.18 billion in 2024 and projected to reach $52.21 billion by 2032 (at a CAGR of 10.1%). This growth is largely driven by increasing demand for SaaS-based, feature-rich property management solutions in both residential and commercial real estate.
Also Read: Best CRM for Solar Businesses
Cost and Pricing Models
How much does property management software cost? Pricing varies widely based on deployment and scale. Unlike one-time licensed software, most PMS today use subscription models (monthly or annual fees). Common pricing factors include: number of units or users, features included, customization level, and type of deployment (cloud vs on-premises). For example, entry-level plans for small portfolios often start quite affordably, whereas enterprise systems for large assets can be costly.
Industry surveys suggest ballpark ranges: entry-level plans for 1–100 units often start around $125 per month, providing basic tenant and rent-tracking features. Mid-tier plans (handling 100–300 units) average about $600–$650 per month, adding portals, enhanced reporting, and payment processing. High-end enterprise solutions (300+ units) can exceed $1,200 per month and include unlimited features, premium support, and compliance modules.
Individual vendors vary greatly. Some offer freemium or low-cost tiers: e.g., RentPost notes that simple packages can be around $50–$100/month for basic functions, while feature-rich enterprise packages can be $500+ per month. Others charge per unit (often a few dollars per unit per month) or per user. Always check if the quote includes implementation, training, and support fees; many providers also charge setup or onboarding fees.
In summary, small landlords may find adequate free or sub‑$100 plans, while corporate managers should budget hundreds to thousands per month for robust systems. The key is matching cost to needs: identify must-have capabilities, estimate your portfolio size and growth, and compare vendors’ tiered pricing (subscription vs per-unit vs per-user) to find the best fit.
Choosing and Implementing the Right System
Selecting the right PMS involves evaluating both current needs and future growth. Important considerations include features, scalability, integration with existing tools, and usability:
- Scalability: Will the software grow with your portfolio? Commercial property owners often need systems that handle thousands of units or multiple asset classes. For instance, a commercial PMS should manage shared expense allocations as your building count rises.
- Integration: Check if the PMS connects to your accounting, CRM, or payment platforms. Seamless integration (e.g. QuickBooks, Sage, bank feeds) reduces manual data entry. Advanced APIs or built-in connectors allow workflows to stay unified; some vendors even integrate with ERPs.
- Customization & Usability: User-friendly interfaces and customization mean the software adapts to your processes, not vice versa. Some platforms (like no-code solutions) let you build custom dashboards or automate niche tasks. Demo each system to ensure your team can use it efficiently.
- Deployment: Cloud (SaaS) vs on-premises is a major decision. Today, cloud solutions predominate for their flexibility and lower upfront cost. But some firms with strict data control policies might choose an on-site system.
- Support & Vendor Reputation: Consider the vendor’s track record and support options. Established companies often have extensive documentation and customer service.
Implementing a new PMS is a process: it requires migrating data (tenant records, leases, financial history), training staff, and possibly re-engineering some business processes. The payoff is long-term efficiency gains. According to experts, companies that plan carefully and choose software aligned with their business see the greatest ROI.
Summing Up
Property management software has become a mission-critical tool for the real estate industry. By digitizing tasks like tenant communication, maintenance coordination, and accounting, a PMS saves managers time and reduces costly errors. The best systems offer powerful features – online rent, reporting, mobile access – and evolve with technology (AI, IoT) to further improve efficiency. Given the growing complexity of managing portfolios, especially in commercial real estate, leveraging the right software is essential.
Evaluating options, consider your portfolio size, property types, and budget. For enterprises needing end-to-end control, custom ERP solutions (as provided by firms like enCloud Solutions) can integrate property management with finance, sales, and operations on one platform. Whichever path you choose, adopting a solid PMS delivers a tangible competitive edge: better tenant relations, accurate financials, and ultimately higher property values. By investing in modern property management technology, owners and managers in the US, UK, and Europe alike can streamline their operations today and stay prepared for tomorrow’s challenges
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What is the primary purpose of property management software?
Property management software automates and centralizes all tasks related to managing rental properties. Its purpose is to simplify operations – from advertising vacancies and screening tenants to handling leases, rent collection, maintenance, and financial reporting. By replacing paper or ad-hoc systems, PMS helps managers work faster, avoid errors, and improve tenant/owner communication.
Who typically uses property management software?
The typical users are landlords, property managers, real estate investors, and management firms handling residential or commercial portfolios. In particular, any owner or agency with multiple properties can benefit. Larger organizations (like real estate investment trusts or commercial building owners) use advanced PMS platforms with sophisticated accounting and compliance features.
What features should I look for in a commercial PMS?
For commercial real estate, essential features include advanced accounting (CAM recovery, CPI adjustments, percentage rents), tenant portals, lease administration for complex contracts, and shared-expense tracking. Integration with financial systems (ERP or accounting) is also important. Also look for strong reporting on occupancy vs. expenses and tools for managing multi-year leases with escalations.
How much does property management software cost?
Costs vary by vendor, deployment, and scale. Entry-level plans might start around $50–$125 per month for very small portfolios. Mid-range systems for hundreds of units often run $600+ per month, while enterprise solutions for large portfolios can exceed $1,000 per month. Some providers charge per unit or per user. Always confirm what’s included (support, updates, implementation) in the quoted price.
Can residential software manage commercial properties?
Generally, no. Residential PMS is built for single-family or multi-family rentals with simple leases and rent collection. Commercial properties have more complex needs – multiple tenants per building, variable lease terms (NNN, gross leases), and detailed expense recoveries. Commercial PMS is designed to handle these complexities (e.g. automating CAM reconciliations and triple-net lease accounting). Using a residential tool for commercial assets often leaves gaps; conversely, using a full commercial system for a single-family rental business can be unnecessarily complicated.
Best Real Estate ERP Software: Streamlining Property Development & Management With Encloud Solutions
The real estate industry faces complex operational challenges: project delays, scattered data, and siloed workflows. During this period of automation, many firms are relying on spreadsheets and disconnected tools for scheduling, accounting, sales, and project management, which causes to financial and operational risk. Manual processes and legacy systems become a hurdle for growing companies, but you can overcome this chellenge by integrating real estate ERP solution as it can break down these silos. Looking to modernize your workflow? Explore our custom real estate ERP solutions today.
ERP real estate software reduces manual effort and speeds up decision-making by unifying finance, assets, and operations. According to an industry analysis, erp for real estate industry integrates and automates verious real estate business operations, which reduces manual efforts and increases efficiency. In short, a real estate management erp helps eliminate errors and delays, which gives managers real-time visibility across projects and finances. Contact our team to see how ERP can transform your real estate operations.
Also Read: Best CRM for Solar Businesses
What is an Real Estate ERP Software?
A real estate development ERP (Enterprise Resource Planning) system is a centralized software platform designed to manage all core functions of a property business. In practice, a ERP system for real estate makes it possible to plan resources, maximize productivity, and control spending by bringing together many applications for different departments. In other words, it acts like a digital “Swiss Army knife” for the company: whether in sales, accounting, procurement, or operations, everyone uses the same unified platform. Schedule a free demo to discover how an ERP can simplify your property management.
For a real estate firm, this means property portfolios, project schedules, contracts, customer leads, and financial data in one system. By implementing a erp for real estate company, companies make everyone’s job easier while keeping greater control over each operation. The system can be scaled as the company grows: as new projects, properties, or sales teams are added, the ERP expands with them. Start your ERP integration journey today and empower your team with real-time data access.
Key Features of the Best Real Estate ERP Software
The best real estate erp software includes features tailored to property and development workflows, like:
- Integrated Financial Management: Unified accounting and budgeting, linking project costs with revenues and cash flow, which ensures accurate expense tracking for construction, leasing, taxes, etc.
- Project and Lease/Booking Management: Tools to schedule project milestones and manage leases or sales bookings. This covers contract creation, renewals, and occupancy tracking for residential, commercial, or mixed-use projects.
- Customer/Agent CRM Portal: A built-in CRM for leads and customers (homebuyers, tenants, brokers), which tracks contacts, inquiries, and communications.
- Marketing and Sales Management: It also contains campaign and promotion tracking features (e.g., emailing prospects, scheduling open houses) to generate leads and follow-up reminders.
- Property/Portfolio Management: A “property bank” to catalog all properties and units that ensures every property’s details (location, status, price) are up-to-date and accessible.
- Transaction and Booking Tracking: ERP software for real estate company also has a module to manage sales, bookings, and payments across multiple projects, with alerts on payment schedules and commission splits.
- Reporting & Business Intelligence: It integrates real-time dashboards and reports on KPIs (sales pipelines, budgets vs. actuals, occupancy rates, etc.) to guide decisions.
- Mobility & Cloud Access: Mobile-friendly interfaces or apps, so agents and managers can view data (leases, client info, financials) on tablets or phones while on site. Interested in these features? Get a personalized walkthrough from our ERP experts.
Industry sources note that a commercial real estate erp often specifically includes features like Customer Portals, Financial Systems, Agent Management, Marketing Management, Property Portfolio (Property Bank), and Booking/Sales Management. The exact feature set can be customized, but all of these focus on automating processes and connecting data across departments.
Figure: Custom real estate management app interface (example). Many modern ERP systems offer mobile dashboards for property and project management on the go.
Also Read: Zoho CRM vs Odoo CRM
Encloud Solutions: Custom Real Estate ERP Software
Encloud Solutions is a development firm that specializes in designing custom ERP, CRM, and web solutions. Their expert team specializes in translating your business goals into customized ERP solutions that optimize operations and drive measurable growth. Reach out to Encloud Solutions to get a custom ERP designed for your real estate business.
Tailored ERP Architecture
Rather than selling a one-size-fits-all package, Encloud emphasizes building software that fits each client’s unique process. As the company states, their team translates “business goals into powerful IT systems” and delivers “tailored ERP solutions for diverse industries, including real estate. In simple words, they devised customized real estate erp modules based on the client’s needs. Book a consultation with Encloud’s ERP specialists today.
Full-Service Implementation and Support
Encloud’s services cover the full ERP lifecycle, from consulting and implementation to data migration and ongoing customization. Need help with ERP implementation? Talk to our experts now.
Odoo ERP
Encloud is a leading partner for Odoo ERP, an open-source platform known for flexibility. They can help you update your Odoo ERP instance with the latest version, so you can enjoy the benefits of new releases, advanced updates, bug fixes, and more. Upgrade your Odoo ERP with Encloud’s certified team and experience the latest performance improvements.
Adapted for Real Estate Operations
In practice, this means Encloud will onboard your existing data (such as past sales or customer lists), configure core modules, and build any extra functionality you require. Their approach is to “design and build systems that adapt to your business”. For a real estate company, Encloud could integrate property sales workflows, automated budget trackers, or landlord-tenant management tools, all within one unified system. This custom real estate erp development ensures you don’t have to force your processes to fit generic software; the software is molded around your processes. Contact Encloud to build an ERP that truly matches your real estate business.
Also Read: ERP for Small Companies
Generic vs. Industry-Specific ERP: Which Is Right?
When choosing an ERP, a key question is whether to use a general-purpose system or one tailored to real estate. In the following table, we discuss the key differences between a generic and industry-specific ERP system.
| Feature | Generic ERP | Industry-Specific ERP |
| Target Audience | Broad industries (e.g., manufacturing, retail, etc.) | Built specifically for real estate development and sales |
| Out-of-the-box Features | Basic modules (HR, finance, inventory) | Real estate-specific modules (leasing, booking, CRM) |
| Customization Needs | High (needs major configuration for real estate) | Low (pre-configured for industry-specific tasks) |
| Implementation Time & Cost | Longer, more expensive due to added development | Shorter, cost-effective, with quicker time to value |
| User Adoption | Lower-level users must adapt to generic workflows | Higher, because the system matches existing business operations |
| Scalability | High, but not optimized for property-specific growth | High, with real estate growth and project scale in mind |
| Integration with Real Estate Tools | May require custom integration work | Often includes prebuilt connectors and APIs |
Benefits of ERP Software for Real Estate Management
If you implement a custom real estate ERP, it yields substantial business benefits that include:
- Centralized Information & Visibility: You can store, track, and analyze all data (financials, projects, customer info, etc.) in one place with an ERP. This consolidated data leads to more accurate reporting and forecasting, since there is no need to manually merge spreadsheets or systems.
- Automation of Manual Tasks: The ERP software handles repetitive processes, automates repetitive/monotonous tasks, and streamlines business processes, which centralizes data, saves time, reduces errors, and frees staff to focus on strategy instead of paperwork.
- Stronger Financial Control: A cloud based real estate erp software ties together cost controls, budgets, and billing. It ensures that project costs, construction expenses, and rental revenues are all tracked against the same financial ledger. This cohesion improves cash-flow management and auditability.
- Improved Customer/Agent Management: Built-in CRM modules help sales and leasing teams serve clients better. For example, erp real estate consulting “helps improve engagement of tenants and stakeholders, enhance customer experience, and strengthen relationships”. Teams can respond faster when all client data (inquiries, contracts, payment history) is at their fingertips.
- Real-Time Decision Making: Because the ERP updates in real time, decision-makers see the latest information. Dashboards and business intelligence tools deliver you an unparalleled financial control and strategic insights for more informed decisions. Managers can quickly spot issues (e.g., a project over-budget) and take action before small problems grow.
- Cost Savings and ROI: Although implementing an ERP is an investment, the long-term payoff is high, as companies minimize their costs by consolidating licenses, reducing manual labor, and avoiding errors. In practice, many real estate firms report lower operational costs, fewer billing mistakes, and higher staff productivity post-ERP. Ready to experience these benefits? Get in touch to start your ERP transformation.
Overall, ERP-driven automation and integration lead to higher efficiency and profitability. One development firm reported a 20%+ boost in efficiency after unifying its accounting, inventory, and asset management through ERP. For real estate leaders, these gains mean faster project delivery, improved tenant satisfaction, and a stronger competitive edge.
Also Read: What Is Property Management Software
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What is an ERP example?
An example of an ERP system is Odoo, which integrates modules for accounting, inventory, CRM, and project management into a single platform. Other common examples include SAP, Oracle NetSuite, and Microsoft Dynamics 365.
How does an ERP work?
An ERP works by integrating key business processes into a unified system with a shared database. This centralization allows different departments (like finance, sales, HR, and operations) to access and update real-time data, which improves collaboration, accuracy, and decision-making.
Is QuickBooks an ERP system?
No, QuickBooks is an accounting software, not a full ERP system. While it handles bookkeeping and financial reporting, it lacks the comprehensive capabilities (like inventory, project management, CRM, etc.) found in an ERP system.
What is ERP in housing?
ERP in housing refers to software systems designed to manage the full lifecycle of residential or commercial properties. It includes features like lease management, tenant CRM, maintenance tracking, project budgeting, and real-time reporting to streamline operations for housing developers and property managers.
Which ERP integrates with real estate CRM systems?
Many ERPs connect directly with real estate CRMs to give one place for managing leads, sales, and property data. Systems like Microsoft Dynamics 365, Odoo, Zoho, and SAP Business One can integrate with real estate CRMs. This helps teams avoid duplicate work, track customer journeys, and get real-time updates on properties and client interactions.
Top tools for real estate with integrated payment solutions?
For real estate businesses, having payments built into the system saves time and avoids delays. Tools like Buildium, Yardi, AppFolio, and Propertyware allow tenants or buyers to pay directly online. They also handle invoices, rent collection, and automated reminders. This reduces manual work and ensures money flows smoothly, while keeping records organized in one place.
What is an ERP?
ERP stands for Enterprise Resource Planning. It’s software that combines different parts of a business into one system, such as accounting, sales, projects, inventory, and HR. Instead of using separate tools for each task, ERP keeps everything connected. For real estate, this means property management, finance, and customer data all work together seamlessly in real time.
Which ERP is best for real estate?
The “best” ERP depends on business size and needs. Yardi and Buildium are popular for property management, especially rentals. SAP and Microsoft Dynamics 365 are strong for larger enterprises needing detailed financials and scalability. Odoo and Zoho are good budget-friendly options for smaller teams. The right ERP is the one that fits your growth and workflow.
Zoho CRM vs Odoo CRM: Features, Pricing & Best Use Cases
Selecting the right CRM is critical for growing businesses. Zoho CRM and Odoo CRM are both mature platforms, but they differ in focus, functionality and deployment model. Zoho CRM is a comprehensive SaaS solution (used by over 50 million users worldwide) with strong out‑of‑the‑box sales and marketing automation, AI-assisted sales forecasting (via “Zia”), and extensive marketplace integrations.
Odoo CRM is part of the modular, open‑source Odoo ERP suite, offering a flexible, integrated approach (Odoo claims 12 million+ users of its apps). Odoo’s CRM emphasizes pipeline management, lead scoring and seamless ties to other business apps (Inventory, Accounting, eCommerce, etc.). Below we compare the two systems across sales, marketing and support modules, as well as integration, scalability and pricing.
Sales Automation
Zoho CRM (Sales Force Automation)
Zoho automates lead capture, scoring and deal management to streamline sales workflows. For example, it provides lead management (lead capture and scoring) and deal (pipeline) management features with stage tracking and reminders. Zoho’s AI assistant Zia can predict sales outcomes and anomalies – e.g. scoring leads, forecasting revenue, and even suggesting sales actions. Key sales features include workflow automation, approval processes (Blueprints), and built‑in telephony (click‑to‑dial, call logging) and social integration. Sales teams get customizable canvases and dashboards, mass email and multi‑currency support. In short, Zoho covers the entire sales cycle “out of the box,” from web-to-lead forms and email campaigns to order quotes and analytics.
Odoo CRM (Sales Module)
Odoo focuses on pipeline visualization and automation. It automatically captures inbound leads from emails, VoIP calls, website forms, social media and event attendees. Sales reps can drag-and-drop leads/opportunities through customized pipeline stages and schedule activities (calls, meetings) from within each opportunity. Odoo’s built‑in scoring and analytics assign a “probability of success” to each lead/opportunity, and integrated email/VoIP support means every email or call log attaches directly to the contact/opportunity. Quotes can be generated in a few clicks with product configurators, and sales orders sync to inventory and invoicing modules (if used). In essence, Odoo CRM provides an end-to-end pipeline tool with tight ERP integration. Want to see how Odoo’s pipeline automation could fit your sales team? Contact Encloud Solutions to book a quick demo or consultation today.
Key Differences: Both platforms offer lead/opportunity tracking, activity scheduling and reporting. Zoho’s strength is its AI‑driven insights (Zia) and rich workflow automation (Blueprints, macros) built specifically for sales teams. Odoo excels when integration with other business areas is needed: for example, quoting in Odoo CRM can automatically pull product/price lists from Odoo Inventory/Sales, and won opportunities flow into Orders. Zoho’s sales UI tends to be more polished for CRM use, while Odoo’s pipeline approach is highly customizable by an administrator or developer.
Also Read: What Is Property Management Software
Marketing Capabilities
Zoho CRM (Marketing)
Zoho CRM includes basic marketing automation features and integrates closely with Zoho’s marketing suite. It supports targeted email campaigns, customer segmentation, and lead nurturing workflows. For instance, you can design mailing lists by segment and schedule drip campaigns to nurture leads at each funnel stage. Zoho also has Google Ads integration (visibility into ad spend vs. sales) and an Event Management module to capture conference or webinar leads. These features work seamlessly with Zoho’s analytics and SalesIQ live chat, giving a complete sales+marketing loop. If deeper marketing automation is needed, Zoho’s separate products (Campaigns, Marketing Automation, Social, Survey) can be integrated.
Odoo CRM (Marketing)
Odoo does not bundle all marketing tools inside its CRM app, but provides a suite of dedicated marketing apps that integrate seamlessly. Odoo Email Marketing lets you design drag‑and‑drop newsletters with templates and track open/click rates. The SMS Marketing app (free with unlimited users) offers high open-rate campaigns – you can segment your database and send scheduled text campaigns to event attendees, subscribers or customers. Other apps like Social Marketing and Events allow posting to social channels and managing event registrations. Crucially, Odoo’s Marketing Automation engine can run cross-channel nurture flows: for example, triggering an email or SMS when a website form is submitted or a sale completes. In sum, Odoo covers email, SMS, social and event campaigns via separate modules, all linked by a unified contacts database.
Support/Service Modules
Zoho CRM (Support)
Within Zoho CRM you get built‑in customer support features. The Cases module handles tickets, solutions (knowledge base articles), and case routing/escalation rules. Web-to-Case forms and email-to-case capture customer requests into the CRM. This means sales and support data live together (for cross-sell and service context). Zoho also offers Zoho Desk as a separate helpdesk product for more advanced service workflows (multi-channel support, customer portal, SLA tracking), which can integrate with Zoho CRM.
Odoo (Helpdesk)
Odoo’s Helpdesk app provides multi-channel ticketing with a kanban overview. It handles support emails, website support forms and even live chat (via the integrated Website Live Chat). You can define custom SLA rules, email templates and canned responses to automate support processes. Odoo Helpdesk also supports selling support contracts (managed in the Timesheets app) and includes a built-in knowledge base (FAQs and community forum links). Customers can even log in to a self-service portal to view or close tickets. In short, Odoo Helpdesk offers a modern ticketing system with SLA automation and self-service, while Zoho CRM’s native support features are more basic (though extendable via Zoho Desk).
App Ecosystem & Integrations
Zoho Marketplace
Zoho CRM benefits from Zoho’s ecosystem of 40+ integrated cloud applications. The Zoho Marketplace alone lists over 900 plug‑and‑play third-party extensions. Built-in integrations cover Google Workspace, Office 365, MailChimp, DocuSign, social networks, telephony (RingCentral, Twilio), and many more. Zoho provides REST APIs, SDKs and low‑code tools (Deluge functions, Web/Mobile SDKs) to customize or connect any system. This makes Zoho CRM extensible for marketing automation, accounting, chat, and other use cases.
Odoo App Store
Odoo is fundamentally an ERP suite, so its CRM is designed to work alongside all other Odoo apps. The Odoo Apps Store offers thousands of modules (many by third‑party developers) covering virtually every business need (from POS to manufacturing). All core Odoo apps are built to integrate – for example, adding the CRM app to your Odoo instance automatically works with Odoo’s Sales, Inventory, Accounting, eCommerce, Email Marketing and more. Odoo supports integration through its open API (XML-RPC/JSON), Odoo Studio customization, and community connectors (e.g. Shopify, Magento, payment gateways). It can also integrate with external systems via REST/JSON APIs or connectors (e.g. Google Docs, shipping carriers). In practice, Odoo’s ecosystem is geared toward one-stop solution (all business processes under one platform), whereas Zoho’s is a mix of Zoho cloud apps plus hundreds of third‑party plugins.
Pricing Overview
Zoho CRM
Zoho’s pricing is per user/per month (billed annually), with a free plan (up to 3 users). The paid tiers are: Standard ($14/user/mo), Professional ($23), Enterprise ($40), and Ultimate ($52). Each adds features (e.g. inventory, Zia AI, advanced customization) and higher data limits. All plans include cloud hosting, while add-ons (extra storage, portals, higher email limits) incur additional fees. Implementation is generally fast with Zoho’s cloud delivery; basic setups can cost as little as $1,000–$3,000, though full enterprise configurations (custom apps, training, data migration) can run into tens of thousands. Zoho’s transparent subscription costs make it predictable, and there are no hidden user-seat minimums.
Odoo
Odoo offers a unique model. The Community Edition is free to download and install (no licensing fee), but does not include official support or some advanced modules. For cloud or supported on‑premise use, Odoo’s paid plans are per-user per month. An “Odoo One App” plan (free) allows unlimited users on any single app (e.g. only CRM). The Standard plan (all apps) starts around $31–$37 per user/month (annual). A Custom plan (~$37–$45) adds multi-company, API and studio tools. All paid plans include hosting, upgrades and unlimited functional support. In practice, small companies sometimes start on Community to save license cost (paying only hosting/partner fees), then move to Enterprise as they need official support or apps. Implementation costs for Odoo can be significant if many modules or customizations are involved; engaging an Odoo partner is common.
Implementation Costs
Zoho’s cloud model often means lower upfront costs (no servers, simpler setup). Odoo’s Community version is free, but both Odoo Community and Enterprise implementations typically involve server costs, partner configuration and possibly custom development. For a fair comparison, include partner fees and data migration expenses.
Also Read: 10 Reasons to Invest in Custom CRM Development for Long-Term Business Growth
Best Use Cases & Recommendations
- Startups and Small Teams: Zoho CRM’s free tier (3 users) and user‑friendly interface make it ideal for startups on a tight budget. It provides core CRM and sales automation immediately. Odoo’s “one-app free” plan can also cover a basic CRM for unlimited users, but requires more tech setup. In general, Zoho often yields faster ROI for a pure sales/marketing focus.
- Growing SMBs: If you need a robust CRM with marketing tools, Zoho’s Professional/Enterprise plans deliver email campaigns, ads integration and AI features at competitive per-user pricing. If you also need ERP features (inventory, accounting, eCommerce) under one roof, Odoo Standard (all apps) could be more cost-effective, and grows with additional Odoo modules.
- Large/Global Enterprises: Odoo shines in complex, multi-company or multi-site environments. Its Enterprise edition supports multiple languages and countries, and can be hosted on-premise for data residency. Zoho CRM Enterprise supports global sales operations with multi-currency and compliance (GDPR, HIPAA), but large companies needing specialized processes (manufacturing, advanced inventory) may find Odoo’s all-in-one model better suited. Encloud Solutions specializes in both Zoho and Odoo enterprise setups — contact us to discuss which solution can best support your global operations.
- Highly Regulated Industries: Zoho has built-in compliance for GDPR and HIPAA, plus mature data security (encryption, SSO). Odoo can be secured as well, but data control comes through on-prem deployments. If strict regulation demands in-house hosting or custom controls, Odoo’s open-source nature offers more flexibility.
- Customization Needs: For bespoke workflows (e.g. custom quoting engines, unique sales processes), Odoo provides more low-level customization (via Odoo Studio or coding). Zoho offers a developer platform and Marketplace apps, but extreme custom features may require extra Zoho products or custom coding by a consultant.
Need a custom CRM tailored to your workflows? Encloud Solutions can develop and deploy both Odoo and Zoho solutions that match your exact business needs. Fill out the form to get a consultation.
| Feature / Aspect | Zoho CRM | Odoo CRM |
| Deployment | Cloud‑only SaaS (no on‑prem) | Cloud or on‑premise (Community or Enterprise) |
| Business Focus | Standalone CRM and sales/marketing automation | Part of integrated ERP suite (CRM + inventory, accounting, etc.) |
| Sales Features | Lead/contact/deal management, forecasting, sales workflows, CPQ | Pipeline management, automated lead capture (email/VOIP/website), AI scoring |
| Marketing Tools | Email campaigns, list segmentation, Google Ads integration, event management | Separate apps: Email Marketing, SMS Marketing, Social, Marketing Automation |
| Customer Support | Cases (tickets), knowledge base, web-to-case, Zoho Desk (add-on) | Helpdesk app: SLA rules, multi-channel tickets, KB, contracts |
| Integrations | 900+ third‑party apps via Zoho Marketplace (Drive, MailChimp, Slack, etc.) | All Odoo modules (Sales, Inventory, Accounting, etc.), plus open API and community connectors |
| Customization | REST API, SDKs, Deluge scripting, low-code Canvas builder | Odoo Studio editor; open-source code; external APIs (XML-RPC/JSON) |
| Pricing (per user) | Free (3 users); $14–52/mo/user (Standard to Ultimate) | Free for 1 app (unlimited users); ~$31–37/mo/user for full suite |
| Typical Use Case | SMBs needing quick CRM deployment, extensive built-in features | Companies needing ERP+CRM integration, custom workflows, manufacturing |
Conclusion and Next Steps
Both Zoho CRM and Odoo CRM are powerful platforms. Zoho CRM offers a user‑friendly, multi‑feature CRM on the cloud, ideal for sales-driven organizations that want fast deployment and rich analytics (with built-in AI/Zia). Odoo CRM offers a more flexible, modular approach, best when CRM must tie directly into other business processes like inventory, accounting or project management. Zoho’s strong points are its extensive integrations and SaaS simplicity; Odoo’s are its open‑source customization and unified ERP ecosystem.
Ultimately, the choice depends on your priorities. For an all-in-one cloud CRM that “just works” for marketing and sales, Zoho CRM is compelling. For a tailored end-to-end business platform (especially if you need ERP functions or have highly specialized needs), Odoo CRM can be the better fit. In practice, many organizations evaluate both: for example, a startup might start on Zoho’s free plan, then migrate to Odoo Enterprise later (or vice versa).
Need guidance? A certified CRM advisor can help match these platforms to your business. Encloud Solutions (encloudsolutions.com) is a trusted CRM implementation partner with deep expertise in both Zoho and Odoo. Their consultants can assess your requirements, run trial deployments, and oversee implementation – ensuring you get the right balance of features, cost and scalability. Whether you lean toward Zoho’s cloud suite or Odoo’s integrated ERP, working with an experienced partner like Encloud Solutions will help you avoid pitfalls and maximize ROI.
Table of Key Differences: The table above summarizes the main distinctions between Zoho CRM and Odoo CRM across key areas. Use it to quickly compare pricing, modules and ideal use cases. Remember that beyond feature lists, real success comes from aligning your CRM choice to your company’s processes, size and industry requirements – and from expert implementation. Both Zoho and Odoo have proven track records; picking the right one often hinges on which ecosystem (Zoho’s cloud apps vs. Odoo’s all-in-one ERP) best matches your vision.
Also Read: Best Real Estate ERP Software